A website is a static or semi-dynamic collection of pages built with HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, offering informational content with minimal user input or real-time data processing. A web application is a dynamic, interactive software accessed via browser that requires authentication, database integration, and complex logic to execute user-driven operations.
The main difference is that a web application emphasizes interactivity and functionality, whereas a website focuses on presenting information. According to IBM Research (2024), over 79% of web applications require user authentication, while less than 18% of websites include login-based features or data interaction. Web applications are also more likely to use backend frameworks such as Node.js, Django, or Laravel for database operations, whereas websites often depend on CMS platforms or static site generators.
The key similarity between a website and a web application is that both are browser-based, use HTML/CSS/JavaScript, support responsive design, and require domain registration, SSL certification, and server hosting for deployment. A study by MIT Web Architecture Lab (2023) found that 100% of web-based systems, regardless of type, must comply with W3C standards and mobile-first responsiveness to maintain accessibility.
Web applications are better than websites in scenarios that require user engagement, real-time interactivity, and backend scalability.
According to Gartner’s 2024 Digital Experience Report, businesses that adopt scalable web applications over traditional websites for user workflows see a 32% increase in operational efficiency and a 27% boost in lead conversion.
What Are the Differences Between a Website and a Web Application?
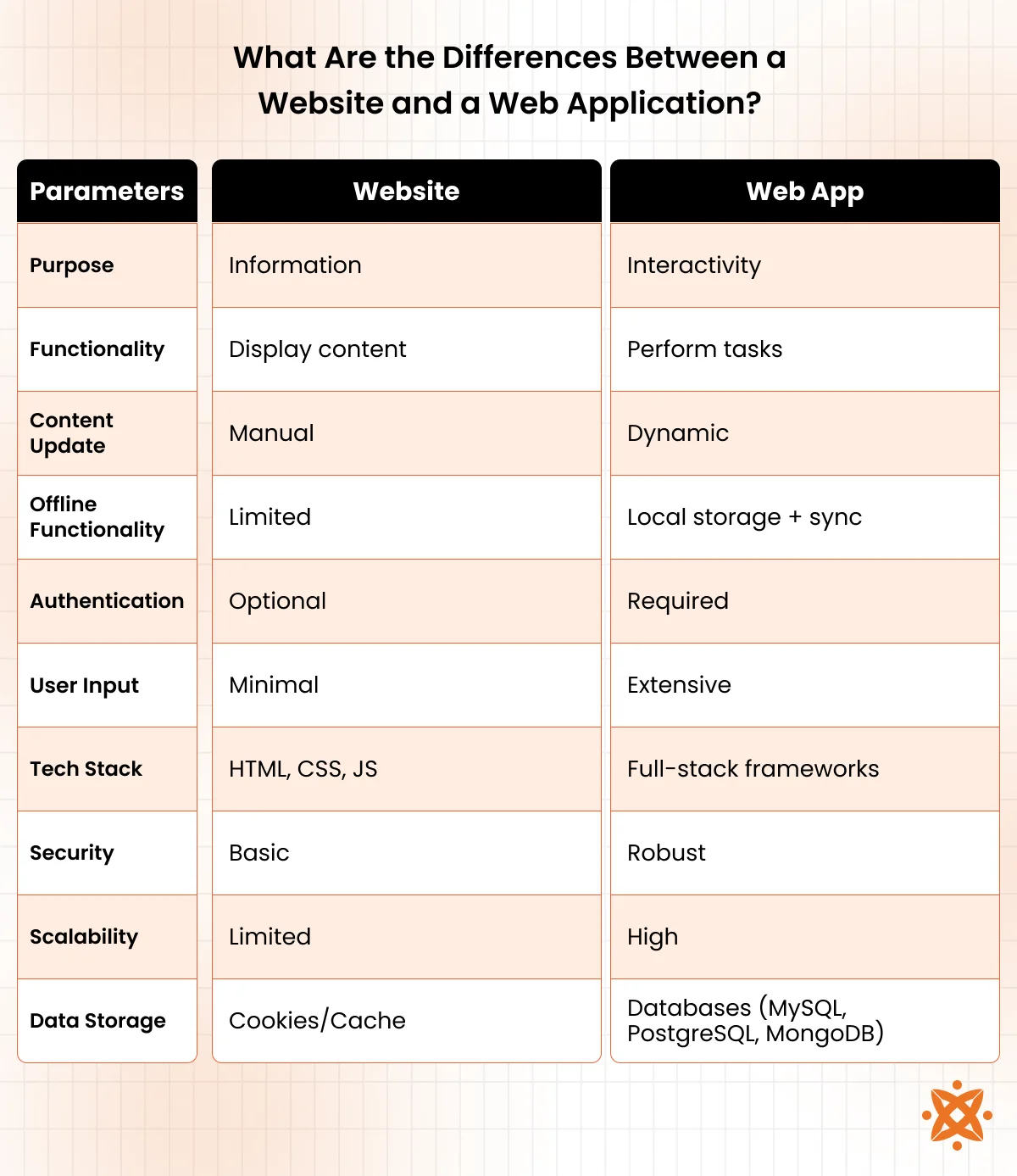
The key differences between websites and web applications include their purpose, functionality, authentication, user input, technology stack, security features, and scalability. These attributes define how they operate and serve users in web development.
Purpose
The purpose of a website is to deliver information. It can act as a digital brochure, portfolio, or publishing platform for news and blogs. A web application is designed for interactivity, enabling user actions, transactions, and dynamic engagement with the interface.
Functionality
Websites are informational tools used to display content to visitors without requiring interaction. Web applications are interactive platforms that allow users to perform tasks and receive real-time feedback.
Content Update
Websites are updated manually, and changes are not immediate. They are suited for information that does not require real-time updates. Web applications update content dynamically and instantly, supporting live data for social media, collaboration tools, and financial dashboards.
Offline Functionality
Websites provide limited offline access, restricted to cached static files. Web applications can store data locally, allow certain tasks offline, and synchronize with the server when connectivity is restored. This supports continuous use in productivity and collaboration platforms.
Authentication
Authentication is optional in websites and is mostly used for admin access or gated content. Web applications require user authentication to access features, data, or services.
User Input
Websites accept minimal input such as form submissions or search queries. Web applications rely on continuous and varied user input to function as intended.
Tech Stack
Websites are built using front-end technologies like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. Web applications use full-stack frameworks combining front-end and back-end tools for dynamic behavior and data management.
Security
Websites follow basic security practices to protect static content and forms. Web applications require robust security to manage user sessions, databases, and sensitive operations.
Scalability
Websites have limited scalability as content updates or user growth do not significantly change system load. Web applications are built to scale, handling more users, features, and data without performance loss.
Data Storage
Websites use minimal data storage, relying on cookies or browser cache for faster loading. Web applications depend on server-side databases such as MySQL, PostgreSQL, or MongoDB to manage user data, application state, and structured information at scale.
What Are the Similarities Between Websites and Web Applications?
The similarities between websites and web applications are based on shared technologies, deployment environments, and design standards.
- Both are browser-based
- Both require internet connectivity
- Both use HTML, CSS, and JavaScript
- Both support responsive design
- Both depend on hosting and domains
- Both follow accessibility and SEO standards
What Is a Website?
A website is a static or dynamic collection of web pages accessible via a browser over HTTP or HTTPS. It is built with HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, hosted on a server, and connected through a domain name. According to Internet Live Stats (2024), there are over 1.1 billion websites globally, though less than 20% are actively maintained.
The core features of a website include structured navigation, published content, multimedia support, and search engine visibility.
Examples of well-known websites include Wikipedia for knowledge, Forbes for business news, Amazon for e-commerce, and Reddit for online communities.
What Is a Web Application?
A web application is interactive software accessed through a web browser that allows user input, requires authentication, and relies on database integration. Unlike static websites, a web app is dynamic and task-driven, supporting CRUD operations such as create, read, update, and delete.
The core features of a web application include real-time interaction, personalized dashboards, and workflow automation.
Examples of popular web apps include Gmail for communication, Facebook for social networking, and Trello for project management.
Is a Web Application Better Than a Website?
No, a web application is not always better than a website, because the better option depends on business goals, cost, and functionality requirements. A website is better when the objective is to provide information, reduce costs, and optimize for SEO visibility. A web application is better when the requirement is interactivity, user authentication, and scalable operations.
When to Choose a Website or a Web Application?
A website is the better option when the goal is information delivery, lower development cost, and SEO visibility, while a web application is preferred when interactivity, authentication, and scalable functionality are required.
- Choose a website when the purpose is sharing information, publishing blogs, or building a corporate portfolio.
- Choose a website when the focus is cost-effective development and achieving search engine visibility.
- Choose a website when minimal user input is needed, such as contact forms or newsletter sign-ups.
- Choose a web application when the requirement is user authentication, database-driven operations, or workflow automation.
- Choose a web application when the business case involves SaaS platforms, CRM systems, or project management tools.
- Choose a web application when scalability and integration with third-party APIs are essential.
The choice depends on aligning business goals with technology requirements. Websites remain cost-effective and SEO-friendly, while web applications provide interactivity, functionality, and long-term scalability.
How to Get Your Website or Web Application Developed?
To get your website or web application developed, first define project requirements such as features, budget, and scalability. You can build with an in-house team, hire freelancers for smaller projects, or choose a professional website development agency. For most businesses, working with an experienced company provides secure architecture, efficient processes, and reliable long-term support.
Is Netflix a Website or Web App?
Yes, Netflix is a web application because it requires authentication, user accounts, and delivers database-driven streaming services with high interactivity.
Is YouTube a Website or Web App?
YouTube functions as both a website and a web application: it offers public video browsing like a website, but personalized dashboards, uploads, and subscriptions make it a web application. As a video platform, it operates in a hybrid model combining user-generated content with interactivity.
Is Facebook a Web App or Website?
Facebook is a web application because it is interactive, requires user login, and provides personalized feeds and messaging features. Its social networking model depends on authentication, database integration, and continuous interactivity.
Is Amazon a Website or Web Application?
Amazon started as a website but is now considered a web application, since it uses dashboards, personalized accounts, and complex transaction systems. As an ecommerce platform, it combines scalability, secure user accounts, and advanced transaction handling.
Is a Web Portal a Website or a Web Application?
A web portal is a web application because it requires authentication, aggregates data from multiple sources, and delivers personalized dashboards to users. Unlike a simple website, a portal manages user roles, database integration, and task-driven interactivity.