E-commerce is the buying and selling of goods or services over the internet, forming the core of digital commerce by enabling businesses to reach customers globally and transact 24/7. It acts as the engine of modern retail, streamlining how products and services are discovered, evaluated, and purchased through digital storefronts.
E-commerce transactions work through a smooth process where users browse products, add them to a shopping cart, and complete purchases via integrated payment gateways. Once payment is verified, order management systems trigger fulfillment, either digital delivery or physical shipping, supported by logistics and customer communication tools.
According to Statista, global e-commerce sales reached $6.3 trillion in 2024 and are expected to surpass $8 trillion by 2027. This growth is fueled by the increasing adoption of mobile commerce, digital payments, and global logistics.
Types of e-commerce business models include B2B (Business to Business), B2C (Business to Consumer), C2C (Consumer to Consumer), and D2C (Direct to Consumer).
The main sales channels for e-commerce include brand-owned websites, online marketplaces like Etsy and Amazon, and social media platforms like Instagram and TikTok. These channels support omnichannel strategies, allowing businesses to meet their customers wherever they shop online.
To launch an e-commerce business, identify a niche and understand your target audience, choose an e-commerce platform, secure a domain, and configure payment and shipping options. Post-launch, tracking analytics and improving the user experience are key to long-term success.
The roles of e-commerce websites include offering a structured space for showcasing products, guiding users through the buying journey, and ensuring secure checkout. They also integrate with payment processors, CRM tools, and analytics platforms to help businesses.
Security risks of e-commerce include payment fraud, phishing scams, data breaches, and non-compliance with regulations like PCI-DSS. Strong cybersecurity measures are essential to protect sensitive user data and maintain trust.
What Is an E-commerce Website?
An e-commerce website is a digital platform where businesses showcase products or services, and customers browse, add items to a shopping cart, and complete purchases through a secure checkout system. It serves as the transactional interface between buyers and sellers, making online sales possible without physical interaction.
At its core, an e-commerce website includes a product catalog, search and filtering tools, payment gateway integration, user account system, inventory management, and customer service features like live chat or support tickets.
Whether you’re selling physical goods, digital products, or services, the e-commerce site acts as your virtual storefront, operational 24/7 and accessible to a global audience.
Why Is E-commerce Important for Businesses and Consumers?
E-commerce is important for businesses and consumers because it enables online shopping through platforms like Amazon, Shopify, and eBay. It allows businesses to sell products or services directly to consumers across the globe, eliminating geographical limits and lowering the costs associated with physical stores. For consumers, it provides the convenience of browsing and purchasing from a digital marketplace anytime, anywhere.
This model simplifies internet transactions, supports real-time inventory tracking, and offers tools for personalized marketing and customer engagement. Whether you’re a small business using Shopify or a large brand leveraging enterprise platforms, e-commerce gives you scalable reach, faster transaction cycles, and access to valuable customer data that informs smarter decisions.
How Does E-commerce Work?
E-commerce works by enabling customers to browse and purchase products through an online store, where items are displayed with descriptions, prices, and availability. When a customer places an order, the platform processes the request through a payment gateway, which securely handles credit cards, digital wallets, or other methods. Once payment is verified, the order is forwarded to the order management system, which coordinates inventory, packaging, and fulfillment.
Behind the scenes, the supply chain and logistics systems ensure the product is shipped and delivered, while customers receive real-time updates on their order status. Technology powers each stage, from product discovery to customer interaction through email or chat, and post-sale support, creating a smooth, automated experience that bridges convenience and reliability.
What Technologies Support E-commerce Operations?
The technologies that support e-commerce operations include content management systems (CMS), payment gateways, inventory management software, and customer relationship management (CRM) tools.
Platforms like Shopify, Magento, and WooCommerce integrate these technologies to ease everything from product uploads to checkout, marketing automation, and real-time analytics.
Below are the technologies that support e-commerce operations:
- E-commerce Platforms: These are the foundation of any online store. Solutions like Shopify, Magento, and WooCommerce help you manage product listings, shopping carts, checkout, and content. A reliable e-commerce software enables you to scale and customize your online storefront.
- Payment Gateways: Services like Stripe, PayPal, and Square process secure payments between buyers and sellers. They ensure payment security by encrypting financial data and supporting fraud detection, giving both you and your customers peace of mind.
- Cloud Computing: Using cloud hosting platforms like AWS, Google Cloud, or Microsoft Azure allows e-commerce websites to run with high availability and speed. It also enables automatic scaling during high-traffic periods, like holiday sales.
- Cybersecurity Solutions: Tools such as SSL certificates, firewalls, and anti-fraud software protect your e-commerce site against data breaches and cyberattacks. These solutions are critical for maintaining trust in online shopping environments.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): CRMs like HubSpot or Salesforce track customer behavior, purchases, and support tickets. They help you personalize marketing and offer better service to retain loyal buyers.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI tools power product recommendations, chatbots, and demand forecasting. It enhances user experience and operational efficiency in AI-driven online shopping platforms.
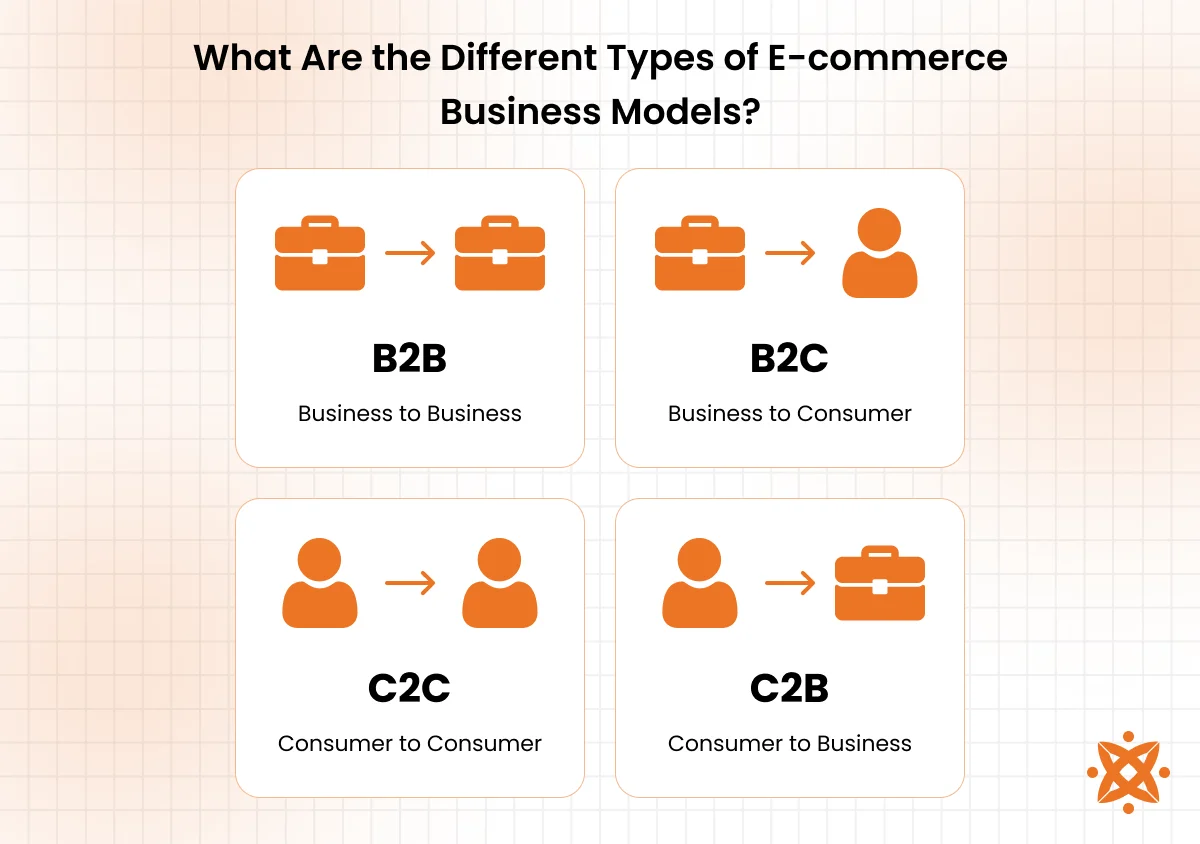
What Are the Different Types of E-commerce Business Models?
The different types of e-commerce business models are B2C (Business to Consumer), B2B (Business to Business), C2C (Consumer to Consumer), and D2C (Direct to Consumer). Each model defines how products or services are exchanged online—whether between companies, individual sellers, or directly from brands to buyers.
Below are the different types of e-commerce business models:
- B2B (Business to Business): In this model, one business sells products or services to another business. It’s common for manufacturers, wholesalers, or SaaS providers. Examples include platforms like Alibaba and Salesforce. B2B e-commerce often involves bulk orders, longer sales cycles, and negotiated pricing.
- B2C (Business to Consumer): This is the most familiar type, where businesses sell directly to consumers through an online store. Think of Amazon, Walmart.com, or a clothing brand’s own Shopify site. B2C transactions are usually quick, involve fixed pricing, and focus on user experience and convenience.
- C2C (Consumer to Consumer): This model allows consumers to sell to other consumers, often facilitated by third-party platforms. Sites like eBay, Craigslist, and Facebook Marketplace are prime examples. Trust and payment protection are crucial in C2C models to ensure secure online transactions.
- C2B (Consumer to Business): Here, individuals offer products or services to businesses. It’s popular in freelancing, influencer partnerships, or crowdsourced product design. Platforms like Upwork and Fiverr are common examples, where consumers pitch services to business buyers.
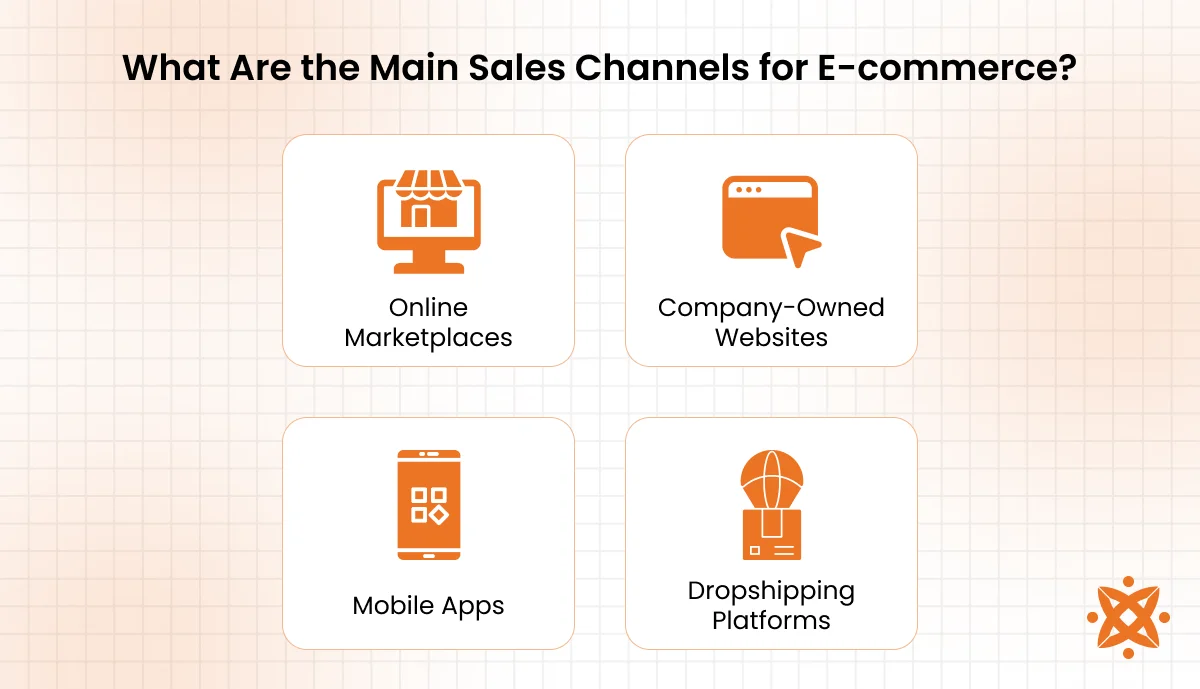
What Are the Main Sales Channels for E-commerce?
The main sales channels for e-commerce are online marketplaces, brand websites, social media platforms, and mobile apps. These channels allow businesses to reach consumers directly, manage their digital storefronts, and drive sales through multiple digital touchpoints.
Below are the main sales channels for e-commerce:
- Online Marketplaces: These are third-party platforms like Amazon, eBay, and Etsy where multiple sellers offer products. They provide built-in traffic and trust, making them powerful tools for digital retail and omnichannel sales.
- Company-Owned Websites: A brand’s own e-commerce website allows full control over branding, pricing, and customer data. This direct-to-consumer model helps businesses build loyalty and personalize the online shopping experience.
- Mobile Apps: Mobile commerce apps offer a streamlined and fast shopping experience. They support push notifications, mobile payments, and personalized UX—key for tapping into the growing mobile-first customer base.
- Dropshipping Platforms: These allow store owners to sell products without holding inventory, with suppliers handling fulfillment. Platforms like Oberlo and Spocket enable fast setup and integration into online marketplaces or company-owned websites.
What Are the Most Common Payment Methods Used in E-commerce?
The common payment methods used in e-commerce include credit/debit cards, digital wallets, bank transfers, and Buy Now Pay Later (BNPL) services. These options offer flexibility and security for online transactions, supporting seamless checkout experiences across global markets.
Below are the common payment methods used in e-commerce:
- Credit/Debit Cards: These are the most widely used forms of payment in e-commerce, allowing customers to pay directly from their bank accounts or via a credit line. According to Statista, credit cards accounted for 34% of global e-commerce transactions in 2023, making them a core driver in payment processing and secure checkout systems.
- Digital Wallets: Digital wallets like PayPal, Apple Pay, and Google Pay store payment details securely and enable quick digital transactions. They are now the leading payment method, responsible for nearly 50% of all global online purchases, due to their speed and encryption-based security protocols.
- Bank Transfers: This method allows customers to transfer funds directly from their bank accounts to merchants. It’s highly secure and used in high-value B2B transactions, though it can lack the instant confirmation that cards or wallets provide.
- Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL): BNPL services such as Klarna and Afterpay allow users to split purchases into interest-free installments. BNPL accounted for over $200 billion in e-commerce transactions globally in 2023, according to McKinsey, proving its role in boosting conversion rates and customer flexibility.
- Cryptocurrency Payments: Cryptos like Bitcoin and Ethereum are emerging as alternative payment methods for tech-savvy consumers. While adoption is still low globally, it’s growing rapidly among retailers looking to reduce transaction fees and support decentralized payment processing.
What Are the Challenges of E-commerce?
The challenges of e-commerce include cart abandonment, cybersecurity threats, and intense competition. These issues affect conversion rates, data privacy, and market share, requiring constant innovation and optimization to maintain profitability and trust.
Below are the challenges of e-commerce:
- Cybersecurity Threats: E-commerce websites are frequent targets of data breaches and cyberattacks, making strong cybersecurity solutions essential to protect customer data and transaction integrity. Without robust e-commerce risk management, even small vulnerabilities can result in significant financial and reputational damage.
- Fraud and Data Breaches: Payment fraud, identity theft, and account takeovers are common in digital commerce. Fraud prevention tools like SSL certificates, two-factor authentication, and AI fraud detection systems are critical in securing e-commerce transactions.
- High Competition: The digital marketplace is saturated, especially in popular niches like fashion, electronics, and beauty. Competing brands rely on aggressive pricing, influencer marketing, and customer loyalty programs to stand out in a crowded space.
- Logistics & Delivery Issues: Shipping delays, incorrect deliveries, and supply chain disruptions can damage customer satisfaction. Effective order management systems and reliable logistics partners are crucial to mitigating these e-commerce supply chain challenges.
- Customer Trust & Retention: Gaining and retaining trust online is harder without physical interaction. E-commerce businesses must offer secure checkout, transparent return policies, and excellent customer service to build loyalty and credibility.
What Are the Key Trends in E-commerce In 2025?
The key trends in e-commerce in 2025 are AI-driven personalization, voice commerce, and sustainable shopping practices. These trends are transforming how online stores enhance user experience, optimize supply chains, and align with eco-conscious consumer values.
Below are the key trends in e-commerce in 2025:
- AI-Powered Personalization: E-commerce platforms now use artificial intelligence to deliver highly tailored shopping experiences, from product recommendations to predictive search, increasing conversion rates and customer satisfaction. This level of automation helps retailers better understand user behavior in real-time.
- Voice Commerce Growth: More consumers are shopping through voice assistants like Alexa and Google Assistant. This hands-free method speeds up search and purchase processes, especially for routine and re-order items.
- Augmented Reality Shopping: AR is revolutionizing digital retail by allowing users to try products virtually, like seeing how a sofa fits in a room or how glasses look on their face. It reduces returns and boosts buyer confidence.
- Sustainable E-commerce: Shoppers now favour brands using eco-friendly materials, recyclable packaging, and carbon-neutral shipping. Companies are adapting by embedding sustainability into their value chain to stay competitive.
How Has E-commerce Evolved Over Time?
Yes, e-commerce evolves historically as a reflection of digital innovation and consumer behavior shifts. It began with the first recorded online transaction in 1994, a Sting CD purchased via NetMarket, and rapidly expanded with the launch of Amazon and eBay in 1995, which revolutionized online marketplaces.
The 2000s introduced secure digital payment systems like PayPal, and by 2010, mobile commerce surged, with over 50% of e-commerce traffic now coming from smartphones and tablets.
Today, AI in e-commerce powers everything from personalized product recommendations to dynamic pricing and predictive inventory, significantly improving customer experience and operational efficiency.
According to Statista, global ecommerce sales exceeded $6.3 trillion in 2024 and are projected to hit $7.5 trillion by 2026, underscoring the sector’s explosive growth and technological advancement in digital payment evolution and mobile commerce.
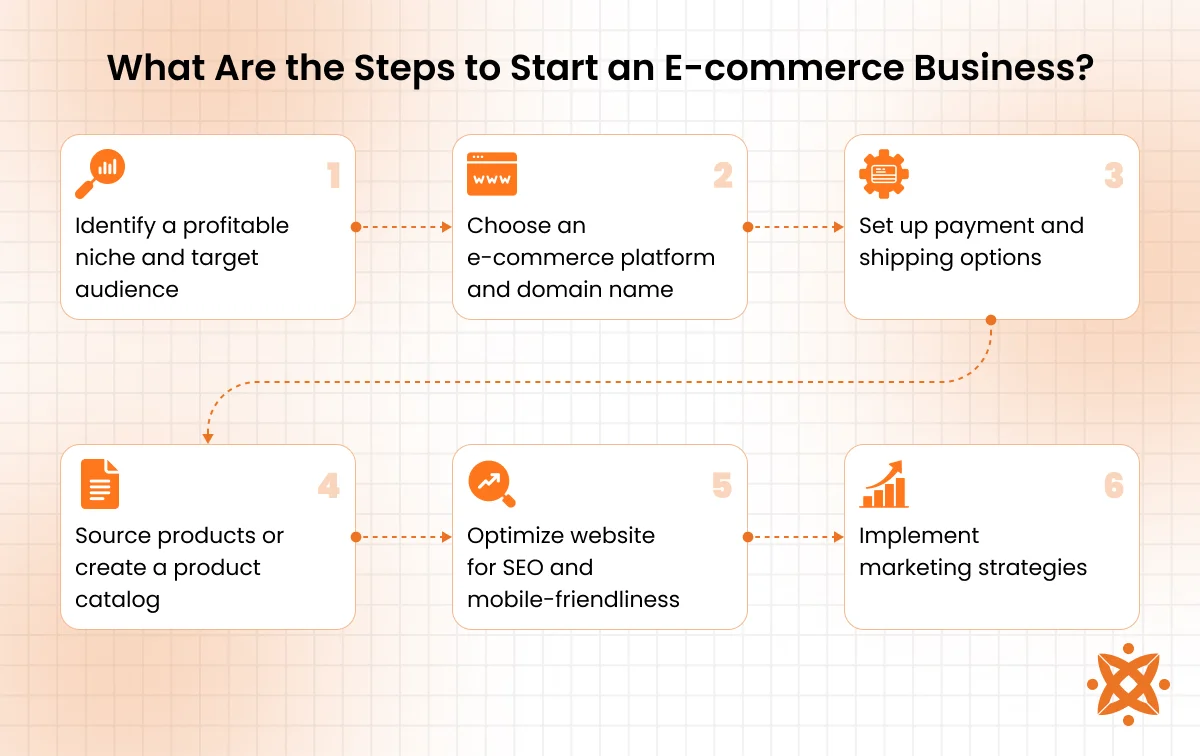
What Are the Steps to Start an E-commerce Business?
The steps to start an e-commerce business are identifying your niche, selecting a business model, setting up your online store, and launching your marketing strategy. You’ll also need to secure a domain name, choose an e-commerce platform, set up payment gateways, manage inventory.
Below are the steps to start an e-commerce business:
- Identify a profitable niche and target audience: Conduct thorough market research to discover gaps in the market or underserved demographics. A clear understanding of your audience will help shape your products, pricing, and messaging, crucial to any ecommerce startup.
- Choose an e-commerce platform and domain name: Select a scalable e-commerce platform like Shopify, WooCommerce, or BigCommerce and secure a domain name that’s memorable and brandable. This forms the backbone of your online store setup.
- Set up payment and shipping options: Integrate trusted payment gateways (like Stripe or PayPal) for smooth transactions, and configure shipping zones, rates, and couriers to streamline your fulfillment process.
- Source products or create a product catalog: Decide whether you’ll manufacture, dropship, or wholesale. Then, structure your product listings with compelling descriptions, images, and categories.
- Optimize website for SEO and mobile-friendliness: Ensure your site loads quickly, uses mobile-responsive design, and includes relevant keywords in titles, URLs, and content to support search visibility and performance.
- Implement marketing strategies: Use a combination of email marketing, social media, influencer collaborations, and paid ads to drive traffic and sales. A solid digital marketing plan is essential for growth.
- Monitor analytics and improve customer experience: Use tools like Google Analytics and Hotjar to track user behavior and conversions. Continuously refine your business strategy based on insights and customer feedback.
It is best to use a professional web developer to start your e-commerce business website. They will ensure that your site is optimized for both SEO and mobile commerce.
What Is the Role of E-commerce Websites in Online Sales?
The role ecommerce plays in website functionality is central to facilitating easy digital shopping experiences. An e-commerce website serves as an online storefront, allowing businesses to display products or services with detailed descriptions, pricing, and availability. It integrates secure checkout processes, including encryption and compliance with payment security standards, to build trust and reduce cart abandonment.
These platforms also connect with payment processors, automate inventory management, and use analytics tools to monitor customer behavior, improving targeting and boosting e-commerce conversions. Overall, they provide a complete system for converting visitors into buyers while maintaining operational efficiency.
How to Develop an E-commerce Website?
To develop an e-commerce website, you need to start by choosing a reliable e-commerce platform like Shopify, WooCommerce, or Magento that suits your business size and technical capacity. Next, secure a unique domain name and connect it to a fast, scalable hosting service to ensure your site is accessible at all times.
The website’s user interface (UI) must be clean, intuitive, and designed for easy navigation, with features like product filters, search bars, and clear calls to action. It’s also essential to optimize for SEO by using proper tags, fast load speeds, and keyword-rich content, while ensuring mobile responsiveness so users on smartphones and tablets get a smooth experience.
Before launch, the e-commerce website development company runs multiple rounds of testing, from usability testing to payment gateway checks, to guarantee everything works flawlessly across devices and browsers.
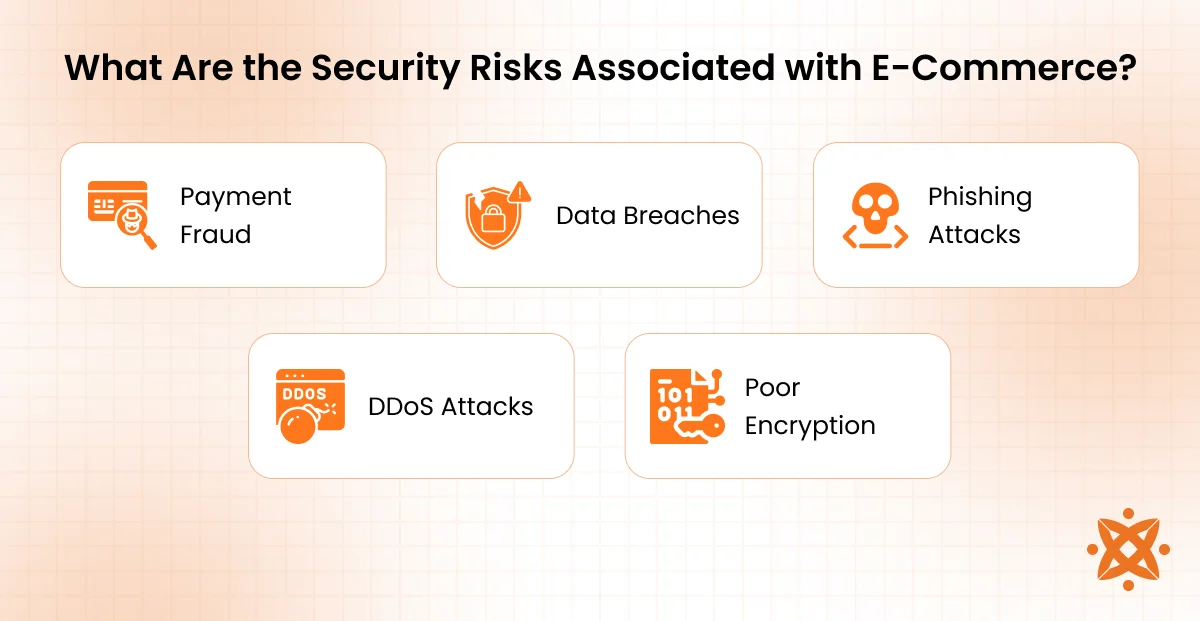
What Are the Security Risks Associated with E-Commerce?
The security risks associated with e-commerce include data breaches, payment fraud, and phishing attacks. These threats compromise sensitive customer information, disrupt operations, and damage your brand’s reputation if proper cybersecurity measures like SSL encryption, firewalls, and secure payment gateways are not in place.
Below are the security risks associated with e-commerce:
- Payment Fraud: Involves the use of stolen credit card data or identity theft, often resulting in chargebacks and financial losses. This is one of the most common cybersecurity threats in e-commerce security, requiring strong fraud prevention tools.
- Data Breaches: Occur when hackers gain unauthorized access to sensitive customer or business data, potentially compromising thousands of records. This threat severely damages a company’s credibility and customer trust.
- Phishing Attacks: Fake emails or websites trick users into giving up login credentials or financial information. These scams are sophisticated and target both shoppers and site admins.
- DDoS Attacks: Distributed Denial-of-Service attacks flood servers with traffic, crashing the site and preventing legitimate transactions. They disrupt online sales and can lead to revenue loss.
- Poor Encryption: Weak or outdated encryption methods put sensitive data, like customer addresses and payment details, at risk. Strong encryption protocols (e.g., HTTPS/SSL) are essential in e-commerce security architecture.
What Is the Impact of Mobile Shopping on E-commerce?
The impact of mobile shopping on e-commerce reshapes how consumers browse, shop, and pay online. Mobile commerce (m-commerce) now accounts for over 60% of total ecommerce sales globally, according to Statista (2024), with app-based shopping, mobile-friendly websites, and digital wallets driving this shift.
Features like one-click payments and autofill checkout forms enhance convenience, while mobile optimization, including responsive design and fast loading speeds, has become a core strategy for improving conversion rates.
Businesses also prioritize mobile SEO, ensuring that their products are discoverable via mobile search, as Google’s mobile-first indexing affects visibility across all devices.
How Does E-commerce Differ from Traditional Retail?
E-commerce differs from traditional retail in how it lowers operational costs, widens customer reach, and offers 24/7 convenience. Unlike brick-and-mortar stores that require physical space and staffing, e-commerce platforms eliminate these overheads, enabling businesses to operate leaner.
Forbes reports that e-commerce businesses save up to 30% in operating costs. It also enables broader access to markets beyond geographical boundaries, giving even small brands global visibility.
Personalization is more scalable in e-commerce, too; platforms like Amazon use algorithms to recommend products based on browsing history. Inventory management is made easy through automation tools, reducing human error and overstocking. This digital transformation gives e-commerce a clear edge in today’s fast-paced, online-driven economy.
How Does AI Integrate into E-commerce?
AI integrates into e-commerce by enhancing the shopping experience through smart recommendations, automated customer support, and predictive inventory management.
Platforms like Amazon use machine learning algorithms to analyse browsing behaviour and deliver personalized product suggestions, contributing to a 35% increase in conversion rates through recommendation engines alone, according to McKinsey.
Chatbots powered by AI, such as Shopify’s Kit or Drift, provide real-time assistance, handle FAQs, and reduce human workload while maintaining 24/7 availability. AI also helps retailers forecast demand, manage stock levels, and automate reordering based on buying patterns, reducing supply chain waste.
These innovations in AI-driven ecommerce continue to reshape how businesses operate and scale in the digital marketplace.