Software development is the structured process of designing, coding, testing, deploying, and maintaining applications or systems that solve real-world problems using computers. It involves turning business or user needs into functional software using programming languages, APIs, and tools like version control systems and continuous integration pipelines.
According to Statista, the global software market is projected to reach $858 billion by 2028, showing its critical role in nearly every industry.
There are several types of software development, including frontend and backend development, mobile app development, desktop software development, cloud computing, embedded systems development, and API integrations.
The main use cases of software development include business automation, e-commerce platforms, web and mobile apps, data management tools, and machine learning systems. As of 2023, over 27 million developers globally build solutions for industries ranging from healthcare to logistics, according to Evans Data Corp.
Common software development methodologies include Agile, Waterfall, DevOps, and Spiral. Agile, the most widely adopted today, breaks work into short sprints, encourages team collaboration, and allows for continuous user feedback.
The software development process follows a structured Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC). It includes steps such as planning, requirements gathering, design, coding, testing, deployment, and maintenance.
What Is Software Development?
Software development is the process of designing, coding, testing, and maintaining software applications. In simple terms, it’s how we build the programs, apps, and systems you use every day, whether it’s the operating system on your laptop, the mobile app you use to order food, or the backend software that runs banks and hospitals. Software development turns ideas into functional digital tools that solve real-world problems.

Software development starts with identifying a need or problem. Developers then plan out a solution, write the code to create the software, test it for errors, and launch it for users. After the release, the software is maintained and updated over time to fix bugs or add new features. This cycle is continuous in most modern software projects, especially with cloud-based or subscription models.
The roots of software development date back to the 1940s, during the early days of computing. One of the first major software programs was created for the ENIAC (Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer), a machine used during World War II.
Over the decades, software development has evolved from writing simple machine-level instructions to creating complex applications using high-level programming languages and powerful development tools.
Here are some quick facts about software development:
- The first high-level programming language, Fortran, was released in 1957.
- There are now over 700 programming languages in existence.
- Agile development, a popular modern methodology, was officially introduced in 2001 with the Agile Manifesto.
- In the U.S. alone, there are over 4.7 million software developers, according to Statista.
What Is Software Design?
Software design is the process of planning how a software application will work before any actual coding begins. It focuses on defining the structure, components, user interfaces, data flow, and overall architecture of the software.
In other words, software design maps out the blueprint for how the software will be built and how users will interact with it. While software development is the entire journey of creating software, from planning and design to coding and deployment, software design is just one phase of that journey.
What Is Software?
Software is a set of instructions, programs, or data that tells a computer or digital device what to do. Unlike physical hardware, software is intangible; it exists as code that powers the functionality of everything from operating systems to mobile apps.
Some everyday examples of software include Microsoft Windows (system software), Google Chrome (application software), Arduino IDE (programming software), and the code inside a smart thermostat (embedded software).
The primary role of software is to make hardware useful. Without software, your laptop, smartphone, or even your car’s onboard computer wouldn’t know how to perform basic tasks.
Software translates human commands into machine language, allowing devices to run smoothly and carry out operations like browsing the internet, managing files, editing photos, or even controlling industrial machinery.
Who Develops Software?
Software is developed by professionals who specialize in planning, writing, testing, and maintaining code. These professionals go by different titles depending on their focus and responsibilities, but they all play a role in turning an idea into working software.
Here’s a breakdown of the key software developer roles:
- Programmers: These are the individuals who write the actual code. They turn software designs and specifications into functional programs using programming languages like Python, Java, or C++. Their job is highly technical and focused on translating logic into machine-readable instructions.
- Software Developers: Developers are responsible for building and maintaining software applications. They’re involved in the full development cycle, from analyzing user needs and designing the software to testing, debugging, and updating. While they write code like programmers, they take on broader responsibilities like project planning and user experience considerations.
- Software Engineers: Software engineers take a more structured and engineering-driven approach. They design scalable and maintainable systems, working on complex software architecture, infrastructure, and integration with other systems. Their job includes applying engineering principles to ensure reliability, performance, and security.
What Are The Benefits Of Software Development?
The benefits of software development are efficiency, innovation, scalability, and competitive advantage. By developing custom software, businesses and individuals automate tasks, solve specific problems, and improve how they operate or deliver value.
Software development isn’t just about writing code; it’s about creating tools that help people and organizations move faster, work smarter, and meet their goals more effectively.
Well-developed software smoothens internal workflows, reduces manual errors, and increases productivity across departments. For customers, it enhances user experience, makes services more accessible, and creates entirely new digital products or platforms.
On a larger scale, software development drives industry growth, supports remote work, powers the digital economy, and enables companies to innovate in ways that were impossible before.
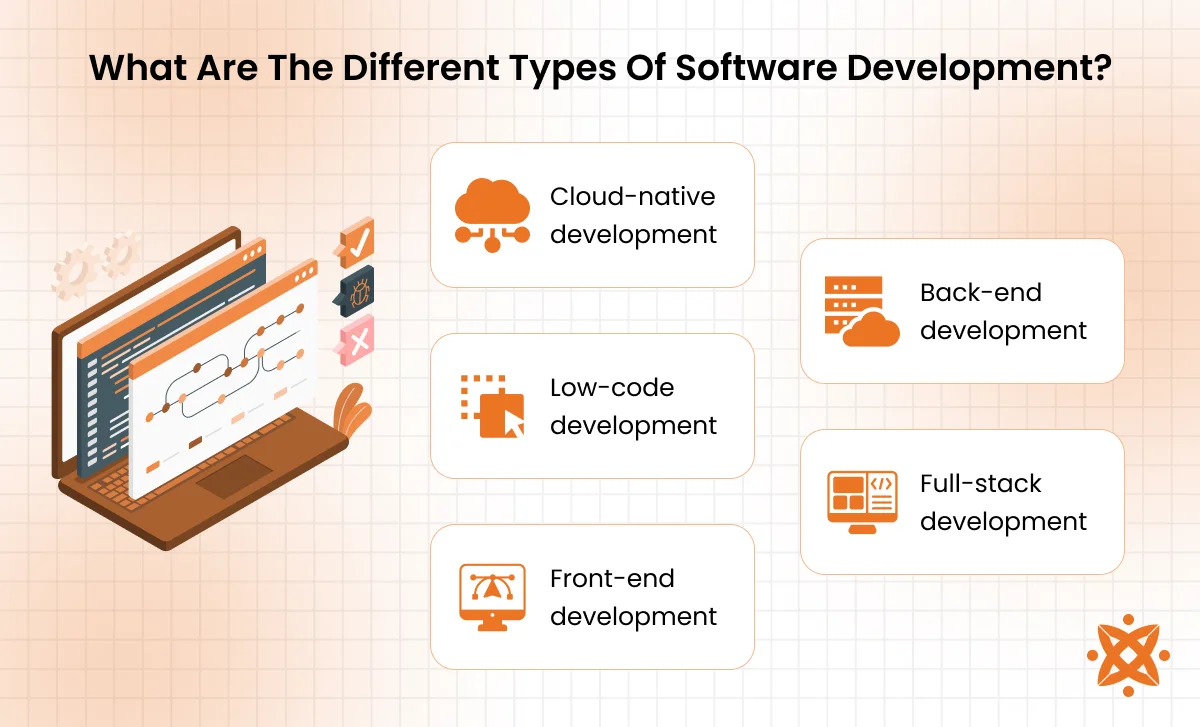
What Are The Different Types Of Software Development?
The different types of software development are cloud-native development, low-code development, front-end development, back-end development, and full-stack development. Each type focuses on a specific layer or approach.
The different types of software development are explained below:
- Cloud-native development: This involves building applications specifically to run in cloud environments like AWS, Google Cloud, or Azure. It uses containers, microservices, and continuous integration to ensure flexibility and speed. These apps scale easily and perform well under varying loads.
- Low-code development: Low-code lets users build software quickly using visual tools instead of hand-coding everything. It’s ideal for teams that want to launch apps faster without deep programming skills. Businesses use it to build internal tools or simple customer-facing platforms.
- Front-end development: Front-end developers build the part of a website or app you see and interact with. They use languages like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript to create layouts, buttons, and animations. Everything from your online shopping cart to your social media feed is front-end work.
- Back-end development: Back-end developers focus on the behind-the-scenes logic that powers apps and websites. They build databases, servers, APIs, and application logic that process user requests. Without the back end, front-end features wouldn’t work properly.
- Full-stack development: Full-stack developers handle both the front end and back end of an application. They understand how to create a complete system from user interface to database. This makes them versatile and especially valuable on small or fast-moving teams.
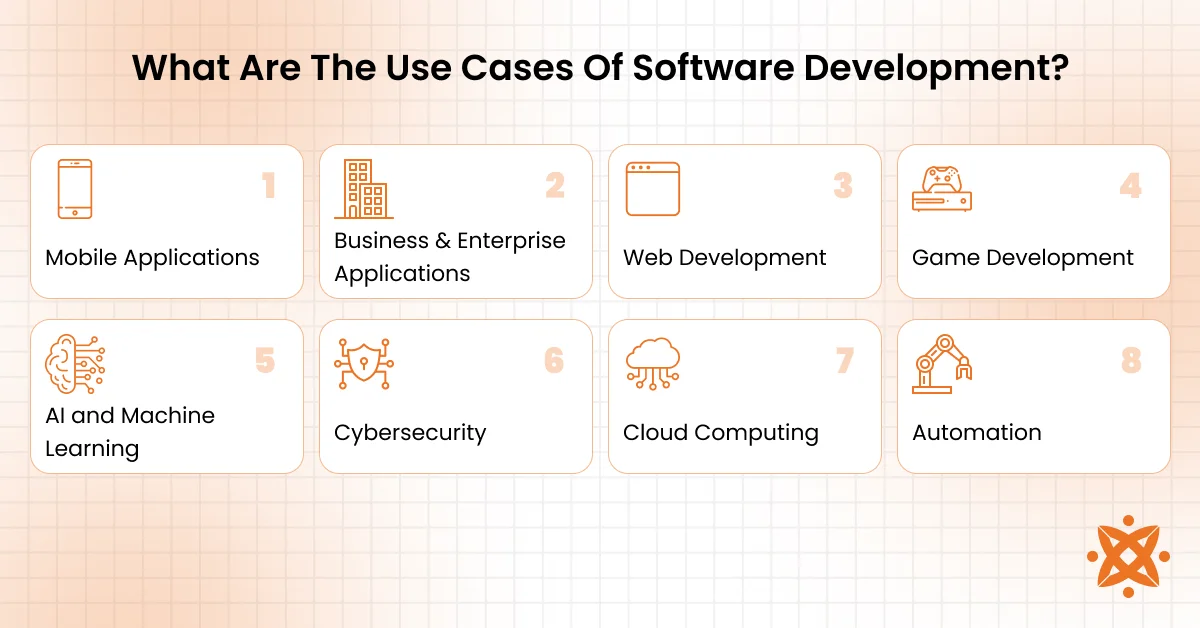
What Are The Use Cases Of Software Development?
The use cases of software development are building digital products, automating business processes, managing data, enhancing customer experience, and enabling remote services.
Whether it’s creating an e-commerce platform, a healthcare app, a CRM system, or a logistics dashboard, software development allows companies to operate faster, smarter, and more efficiently across nearly every industry.
The following are the use cases of software development:
1. Mobile Applications
Mobile application development focuses on creating software specifically designed to run on smartphones and tablets, using operating systems like iOS and Android. This type of development includes both native apps, built for a single platform using languages like Swift or Kotlin, and cross-platform apps, which use frameworks like Flutter or React Native to work across multiple devices.
These mobile applications range from simple utilities like calculators and note apps to complex platforms like mobile banking, fitness trackers, or social media apps. For example, apps like Uber, WhatsApp, and TikTok are all mobile-first products that rely heavily on efficient software development to deliver smooth and responsive user experiences.
2. Business and Enterprise Applications
Business and enterprise software is built to support internal operations, improve workflows, and enable large organizations to run efficiently. This category includes applications like CRM systems (e.g., Salesforce), ERP software (e.g., SAP), and HR tools that manage payroll, recruitment, and employee performance.
Enterprise software requires integration with other systems, scalability for large teams, and compliance with industry regulations. Developers working on these projects must prioritize security, data integrity, and long-term maintenance, especially for companies in finance, healthcare, or government sectors.
3. Web Development
Web development is the process of building software that runs in web browsers. This includes everything from static websites to full-scale web applications. Front-end developers handle what users see and interact with (HTML, CSS, JavaScript), while back-end developers manage server-side logic, databases, and APIs.
Popular examples include platforms like Amazon, Facebook, and Google Docs. Web development is one of the most common use cases because it makes software accessible on any device with internet access, and it’s the first point of contact between a business and its customers.
4. Game Development
Game development focuses on creating interactive digital games for platforms like consoles, PCs, or mobile devices. This involves designing gameplay mechanics, creating graphics and sound, coding game logic, and optimizing performance.
Game developers often use engines like Unity or Unreal Engine, which allow them to build immersive experiences with realistic visuals and real-time interaction. Whether it’s a mobile puzzle game or a large-scale multiplayer game like Fortnite, this type of development demands creativity, precision, and technical expertise.
5. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning software development involves creating systems that learn from data and make decisions with minimal human intervention. Developers build models that identify patterns, predict outcomes, or automate tasks, such as chatbots, recommendation engines, and fraud detection systems.
Examples include tools like Google Assistant, Netflix’s recommendation engine, and financial institutions’ credit risk analysis software. This use case is growing rapidly as more businesses invest in data-driven solutions to improve efficiency and personalize user experiences.
6. Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity software is designed to protect systems, networks, and data from unauthorized access, breaches, or attacks. Developers in this field create firewalls, antivirus tools, encryption protocols, and security monitoring platforms.
Companies like Norton, McAfee, and CrowdStrike develop solutions that detect and respond to threats in real time. As cyberattacks become more sophisticated, the demand for secure, up-to-date security software continues to rise across all industries.
7. Cloud Computing and Infrastructure
Cloud software development enables businesses to host applications and store data on remote servers rather than on-premises hardware. This includes building tools for cloud storage, virtual machines, container orchestration, and serverless applications.
Services like AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud offer platforms for building and scaling cloud-based software. Cloud infrastructure helps businesses reduce IT costs, increase flexibility, and improve system uptime, making it essential for modern, globally distributed teams.
8. Automation
Automation software helps eliminate repetitive tasks by using scripts, bots, or workflow tools to perform actions automatically. This is widely used in fields like finance, marketing, manufacturing, and customer service.
Examples include automated billing systems, email marketing tools like Mailchimp, and robotic process automation (RPA) tools such as UiPath. By reducing manual labor, automation software increases speed, consistency, and cost-effectiveness.
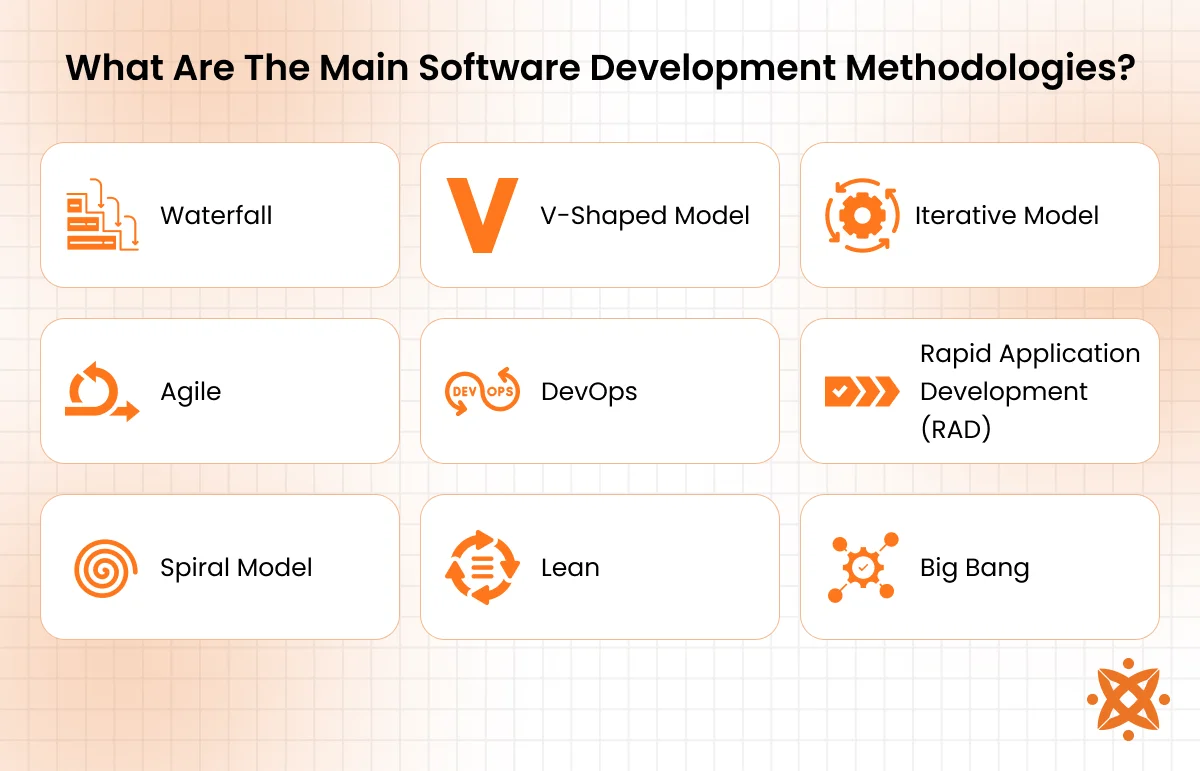
What Are The Main Software Development Methodologies?
The main software development methodologies are Waterfall, Agile, DevOps, V-shaped, Iterative, Rapid Application Development (RAD), Spiral, Lean, and Big Bang. Each approach offers a different way of managing and executing a project.
The following are the main software development methodologies:
- Waterfall: Waterfall is a linear and sequential approach where each phase of development (requirements, design, implementation, testing, deployment, maintenance) must be completed before the next begins. It’s best used when project requirements are well-defined and unlikely to change. This method is easy to manage but lacks flexibility once development is underway.
- V-Shaped Model: The V-shaped model extends the Waterfall method by pairing each development stage with a corresponding testing phase. It emphasizes validation and verification early in the process. It’s structured and risk-averse but still rigid and not ideal for dynamic projects.
- Iterative Model: In the Iterative model, software is developed and improved through repeated cycles (iterations). Each version adds functionality until the final system is complete. It allows for testing and feedback early, which helps uncover problems before the project is too far along.
- Agile: Agile is a flexible, collaborative approach that delivers software in small, working increments called sprints. It allows teams to adapt quickly to changes and feedback. Agile is ideal for projects where requirements evolve over time, promoting frequent releases and user involvement.
- DevOps: DevOps combines software development (Dev) and IT operations (Ops) to shorten the development cycle and increase deployment frequency. It focuses on automation, continuous integration, and continuous delivery (CI/CD). This method improves speed, collaboration, and reliability in delivering software.
- Rapid Application Development (RAD): RAD emphasizes quick prototyping and rapid feedback over long development cycles. It’s useful when speed is more important than perfection, especially in startups or proof-of-concept scenarios. However, it requires highly skilled developers and consistent user involvement.
- Spiral Model: The Spiral model combines elements of both design and prototyping in a risk-driven process. Projects are divided into smaller parts and each part goes through a spiral of planning, risk analysis, engineering, and evaluation. It’s ideal for large, complex, high-risk projects.
- Lean: Lean software development focuses on maximizing value while minimizing waste. It emphasizes continuous improvement, fast delivery, and respect for the team. Lean encourages simplicity and only builds what’s necessary based on customer needs.
- Big Bang: Big Bang development starts with minimal planning and moves directly into coding. It works best for small projects or experimental builds where the requirements are flexible or undefined. This model is risky for larger, structured projects due to lack of predictability.
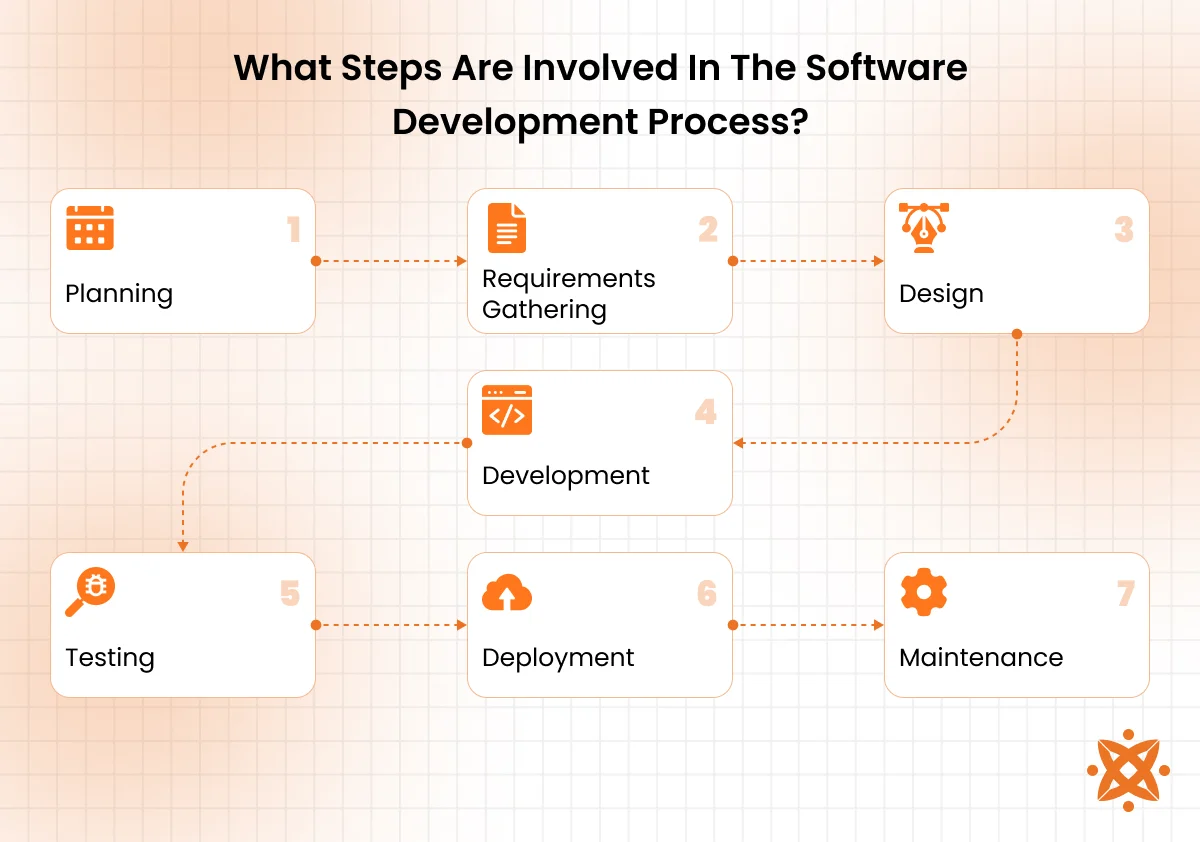
What Steps Are Involved In The Software Development Process?
The 7 steps involved in the software development process are planning, requirements gathering, design, development, testing, deployment, and maintenance. These steps are part of the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC), a structured framework that helps teams build high-quality software systematically and predictably.
The 7 steps involved in the software development process are as follows:
1. Planning
Planning is the first and most strategic phase where goals, timelines, and resources are defined. The development team works with stakeholders to outline what the software is expected to achieve and how the project will be managed. A clear plan helps avoid scope creep and sets expectations from the beginning.
2. Requirements Gathering
In this step, developers and business analysts collect detailed information about what the users need the software to do. Functional and non-functional requirements are documented, such as performance expectations, security needs, and system features. The requirement gathering phase ensures everyone is on the same page before design begins.
3. Design
Software architects and designers use the requirements to create the system architecture and user interface layouts. They decide how the software will look, how it will be structured, and how different components will interact. Wireframes, technical diagrams, and mockups are typically produced during this phase.
4. Development
Development is the coding phase where developers build the software according to the design specs. Front-end and back-end code is written, databases are connected, and features are implemented. It’s the longest phase and includes version control, internal testing, and frequent reviews.
5. Testing
Before the software is launched, it goes through rigorous testing to find and fix bugs or performance issues. This includes unit testing, integration testing, system testing, and user acceptance testing. The goal is to ensure the software is stable, secure, and functions as intended.
6. Deployment
Once testing is complete, the software is released to users through either a public launch or a private rollout. This phase involves configuring servers, migrating data, and monitoring for any unexpected errors. In some cases, it’s done in stages to reduce risk.
7. Maintenance
After deployment, the software enters the maintenance phase, where updates, bug fixes, and performance improvements are made over time. User feedback is also collected to guide future changes. Maintenance is ongoing and ensures the software continues to meet evolving needs.
What Is The Difference Between Software Development And Programming?
The difference between software development and programming is scope. Programming refers specifically to the act of writing code, turning logic into machine-readable instructions using a programming language.
Software development, on the other hand, is a broader process that includes planning, designing, coding, testing, deployment, and maintenance. In short, programming is just one part of the full software development lifecycle.
While a programmer focuses on solving individual problems with code, a software developer manages the entire process of creating a functioning, user-ready product.
What Is The Difference Between Software Development And App Development?
The difference between software development and app development is the scope of the product being built. Software development is a broad term that includes creating all kinds of software, whether it’s a desktop program, web application, backend system, or enterprise solution.
App development, however, typically refers to building applications for mobile devices or specific user-facing platforms like Android, iOS, or Windows. While all apps are software, not all software qualifies as an “app,” especially when it’s designed for internal systems or backend operations without a user interface.
What Is The Difference Between Software Development And Web Development?
The difference between software development and web development is the platform and scope of the solution being built. Software development covers the entire process of creating software for any environment, this includes desktop applications, mobile apps, embedded systems, and cloud services.
Web development, in contrast, is focused specifically on building software that runs inside a web browser, such as websites and web applications. While web development is a type of software development, it’s narrower in focus and involves front-end (user interface) and back-end (server logic) technologies used for online platforms.
Can AI Be Used In Software Development?
Yes, AI can absolutely be used in software development, and it’s already transforming the way code is written, tested, and deployed. AI-powered tools are helping developers generate code snippets, detect bugs, suggest improvements, and even automate entire workflows.
For instance, GitHub Copilot, powered by OpenAI, autocomplete lines or entire functions based on natural language prompts, speeding up development and reducing repetitive work.
As of 2024, over 30% of developers use AI tools weekly, according to Stack Overflow’s Developer Survey. Beyond productivity, AI enhances quality by flagging security risks and performance bottlenecks early in the process.
How To Choose A Development Software Company?
To choose a software development company, you need to focus on experience, technical expertise, communication, and business alignment. Start by reviewing their portfolio, look for projects similar to yours, and check if they’ve built solutions in your industry or technology stack.
Also, evaluate their development process. Do they follow best practices like Agile or DevOps? Are they transparent with timelines, pricing, and deliverables? Good companies will offer clear project management tools, assign a dedicated team, and maintain open communication throughout the engagement.
Finally, make sure they understand your business goals, not just the technical requirements. A great software company builds products that actually solve real problems, not just write code.
What Are The Software Development Best Practices?
The software development best practices are writing clean code, using version control, automating testing, following a defined workflow, and prioritizing user needs. These practices help reduce errors, speed up development, and create software that performs well and scales reliably.
A good software development company starts with clean, readable, and well-documented code so others can easily understand and maintain it. Version control systems like Git let teams track changes and collaborate without overwriting work.
Testing, especially automated unit and integration testing, catches bugs early before they become expensive problems. Teams should also follow structured workflows like Agile or DevOps for better coordination, and always design with the user in mind by validating features through feedback and usability testing.
What Is The Cost Of Developing Software?
The cost of developing software ranges from $5,000 to over $500,000, depending on the complexity, features, and team involved. Simple apps or MVPs (Minimum Viable Products) might cost between $5,000–$25,000, while enterprise-grade systems or platforms with complex integrations, custom design, and ongoing support can easily exceed $250,000 or more.
Several factors affect cost, including project scope, development time, tech stack, location of the development team (U.S. vs offshore), and whether you’re hiring freelancers or an agency. For example, hourly developer rates in the U.S. range from $75 to $150, while offshore teams charge $25 to $60 per hour.
Add in design, project management, QA testing, and maintenance, and the total cost varies widely based on your exact needs.
How Long Does Software Development Take?
Software development takes anywhere from 4 weeks to over 12 months, depending on the project’s size, complexity, and available resources. A basic mobile or web app with limited features takes 1 to 3 months, while a large-scale enterprise platform with complex functionality can stretch over 6 to 12 months or more.
Timelines are also influenced by the number of developers involved, the use of Agile vs. Waterfall methodologies, and how clearly defined the project requirements are. Delays occur when scope changes mid-project or when there’s insufficient communication between stakeholders and the development team. Proper planning, testing, and phased releases help keep the project on track.
What Is The Role Of AI in Software Development?
The role of AI in software development is automation, acceleration, and quality improvement. AI helps developers write code faster, catch bugs earlier, and deploy software more efficiently by learning patterns, generating suggestions, and handling repetitive tasks.
For example, AI tools like GitHub Copilot and Amazon CodeWhisperer can generate lines of code based on natural language inputs, saving hours of manual programming. AI also powers intelligent testing systems, automated documentation tools, and predictive analytics that help teams make data-driven development decisions.
Beyond coding, AI assists in project management, effort estimation, and user behavior modeling, all of which contribute to faster, smarter, and more reliable software delivery.
The Role Of DevOps in Modern Software Development
The role of DevOps in modern software development is to unify development and operations, automate workflows, and speed up software delivery without sacrificing quality. DevOps breaks down the traditional silos between developers and IT operations teams, allowing them to work together throughout the entire software lifecycle.
DevOps practices like Continuous Integration (CI) and Continuous Deployment (CD) ensure that code changes are tested and pushed live frequently and reliably. Tools like Jenkins, Docker, and Kubernetes help automate these processes, reduce human error, and make applications more scalable.
By adopting DevOps, companies release software faster, respond to user feedback quickly, and maintain high levels of system stability and performance.
What Is The Role Of Ux Design In Software Development?
The role of UX (User Experience) design in software development is to ensure the software is easy to use, visually intuitive, and aligned with user needs. UX design focuses on how users interact with a product. It aims to make that experience smooth, engaging, and frustration-free. It’s not just about looks; it’s about function, flow, and feedback.
During development, UX designers create wireframes, user journeys, and prototypes to map out how people will navigate the software. They also test interfaces with real users to catch problems before launch. When UX is done right, it increases user satisfaction, reduces churn, and directly improves the product’s success in the market.
How To Balance Speed Vs Quality In Software Development?
To balance speed vs quality in software development, you need to adopt smart planning, prioritize features, and use automation to maintain standards without slowing down delivery. The key is not choosing one over the other, but designing a process that supports both, building fast without breaking things.
Start by defining a clear MVP (Minimum Viable Product) so your team focuses on essential features first. Use Agile or Scrum to break work into sprints, allowing for constant review and adjustment.
Implement automated testing and CI/CD pipelines to catch bugs early without manual delays. Most importantly, don’t skip code reviews or user testing, speed is wasted if the product doesn’t work as expected or frustrates your users.
What Are The Common Myths About Software Development?
The common myths about software development include: it’s just about coding, it can be done quickly if the developer is good enough, and once the software is built, it’s finished. These ideas sound reasonable on the surface but lead to confusion, poor planning, and unrealistic expectations.
First, software development is much more than just writing code, it involves planning, design, testing, deployment, and maintenance. Second, speed doesn’t always equal quality; even great developers need time to build stable, secure, and user-friendly software. And finally, software is never truly “done,” updates, bug fixes, feature requests, and tech upgrades keep the cycle going long after launch.
What Are The Latest Trends In Software Development?
The latest trends in software development include AI-assisted coding, low-code/no-code platforms, cloud-native development, microservices architecture, and increased focus on cybersecurity. These trends are shaping how software is built, who builds it, and how quickly it can reach the market.
AI tools like GitHub Copilot and ChatGPT are now helping developers write, refactor, and document code faster than ever before. Meanwhile, low-code platforms such as OutSystems and Microsoft Power Apps allow non-developers to build functional applications with drag-and-drop interfaces.
Cloud-native approaches, using tools like Kubernetes and serverless functions, make apps more scalable and resilient. Developers are also embracing microservices to build flexible, modular applications instead of monolithic systems.
And with rising cyber threats, there’s a growing demand for secure-by-design development, where security is embedded into every phase of the SDLC.








![IT Outsourcing: Statistics, Cost, Types, Models & Locations [2024 Guide]](https://www.intelivita.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/it-outsourcing-statistics-cost-types-models-locations-complete-guide-2024-1024x576.webp)





