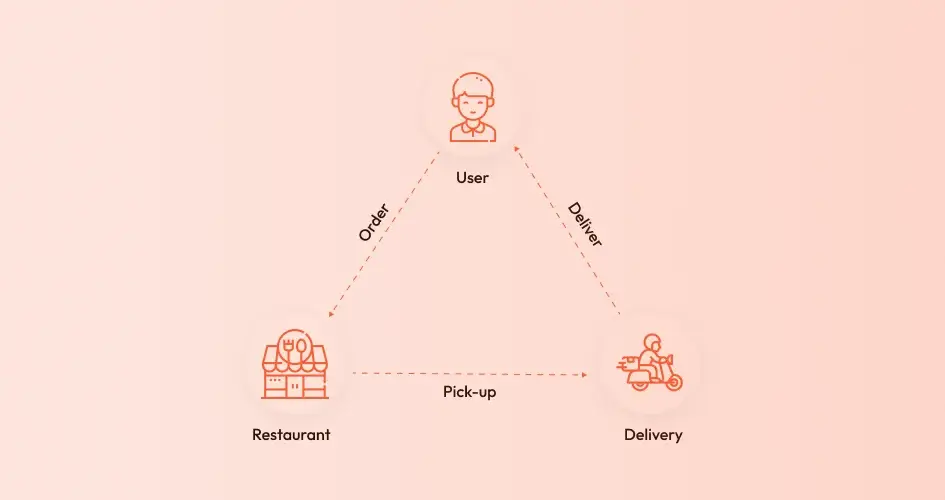
A food delivery app refers to a mobile platform that allows users to order meals from nearby restaurants and get them delivered to their doorsteps. It handles everything from menu browsing to payment and delivery tracking, streamlining the entire process via mobile.
The three main types of food delivery apps are aggregator apps, dedicated restaurant apps, and logistics support apps. Aggregator apps like Grubhub let users browse multiple restaurants, dedicated apps like Domino’s are built for individual brands, while logistics-focused apps like DoorDash handle the delivery side using their own fleet.
Core features of a food delivery app include user registration, menu browsing, order placement, payment integration, real-time order tracking, and push notifications. These functionalities are essential for delivering a seamless user experience, especially on iOS, Android, and cross-platform environments.
Food delivery apps provide users with convenience and speed, while restaurants benefit from increased reach and revenue. In 2024, over 215 million users in the U.S. used food delivery apps, contributing to a market value exceeding $66 billion (Statista, 2024).
The development process for a food delivery app includes UI/UX design, front-end and back-end coding, API integration, and testing. Apps are usually built for iOS and Android or via cross-platform tools like React Native to ensure broad accessibility.
The cost to build a food delivery app ranges from $60,000 to $300,000, depending on complexity and location. Major cost factors include UI/UX design, front/back-end development, API integrations, testing, and cloud infrastructure setup.
What Is a Food Delivery App?
A food delivery app is a mobile or web-based application that lets users order meals or groceries from local restaurants or stores and have them delivered to their doorstep. These apps act as intermediaries between customers, restaurants, and delivery drivers, streamlining the entire ordering process.
Instead of calling a restaurant, you can browse menus, customize orders, make payments, and track deliveries, all from your phone or computer.
The typical food delivery app includes features like a restaurant listing page, menu view, cart system, delivery tracking, and payment gateway. On the backend, it connects restaurant dashboards, customer accounts, and driver dispatch systems to handle everything in real time.
Food delivery apps have become a massive part of daily life in the U.S. According to Statista, the U.S. online food delivery market is expected to reach $66.56 billion in revenue by the end of 2025, with over 217 million users. Apps like Uber Eats, DoorDash, and Grubhub dominate this space, accounting for thousands of deliveries every minute.
What Are the Different Types of Food Delivery Apps?
The different types of food delivery apps include aggregator apps, location apps, and dedicated apps. Aggregator apps like Grubhub connect users to restaurants but leave the delivery to the restaurants, while delivery platforms like Uber Eats handle both ordering and delivery through independent couriers.
The different types of food delivery apps are explained below:
Aggregator Apps
Aggregator apps act as third-party platforms that connect users to a wide range of restaurants. Their main function is to let users browse menus, place orders, and pay — while the restaurant handles the actual delivery.
Examples of aggregator apps include:
- Grubhub
- Seamless
- EatStreet
- Delivery.com
- OpenTable (limited delivery features)
Dedicated Restaurant Apps
Dedicated restaurant apps are built specifically for one restaurant or chain. These apps give full control to the restaurant, from menu design to promotions and delivery options.
Examples of dedicated restaurant apps include:
- Domino’s
- Chick-fil-A
- McDonald’s
- Chipotle
- Starbucks
Logistic Support Apps
Logistic support apps focus purely on the delivery process. They allow restaurants or marketplaces to outsource delivery without building a full-fledged ordering app.
Examples of logistic support apps include:
- Uber Eats
- DoorDash Drive
- Postmates
- Relay Delivery
- Skipcart
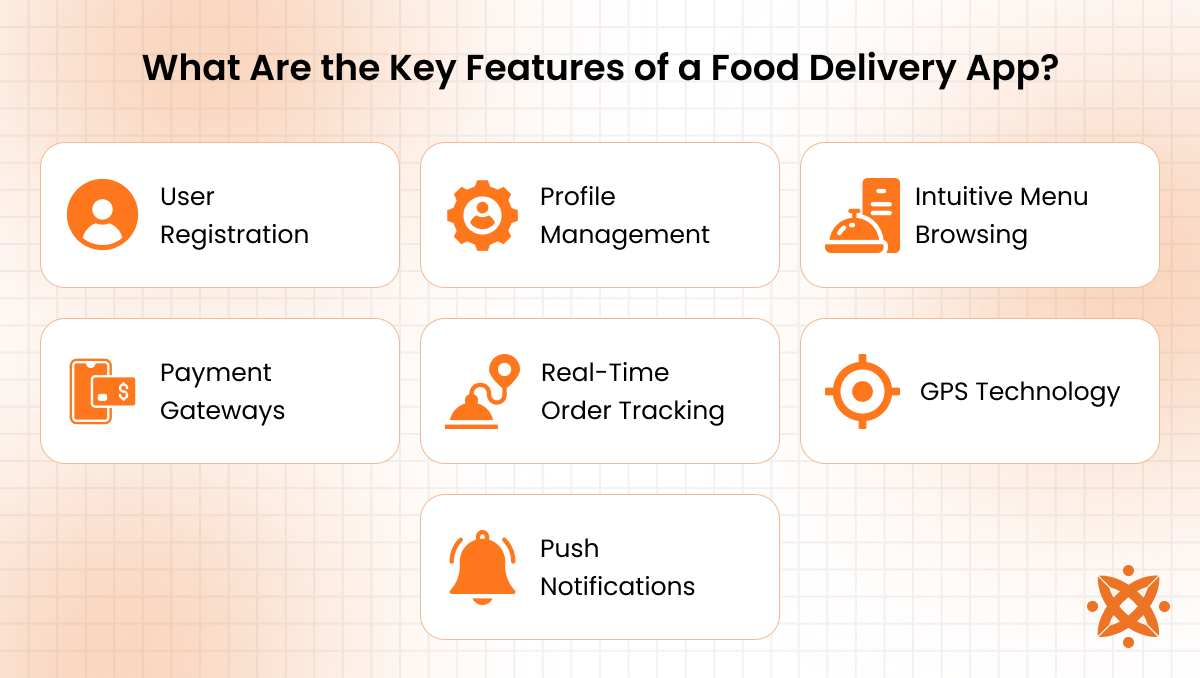
What Are the Key Features of a Food Delivery App?
The key features of a food delivery app are real-time order tracking, easy payment options, restaurant search and filters, user profiles, and push notifications. These features make the app functional, user-friendly, and efficient for both customers and restaurant partners.
The key features of a food delivery app are explained below:
- User Registration: Users need a simple and secure way to sign up, through email, phone number, or social accounts. This step helps personalize the experience and track orders efficiently.
- Profile Management: Customers should be able to edit their details, save addresses, and manage preferences. A flexible profile system also helps with loyalty rewards and saved payment methods.
- Intuitive Menu Browsing: The app should allow easy navigation through restaurant listings, categories, and food items. Menus must be clean, searchable, and include images, pricing, and options.
- Payment Gateways: A good app integrates multiple secure payment options like credit cards, PayPal, and Apple Pay. This flexibility encourages more purchases and builds user trust.
- Real-Time Order Tracking: Users want to see where their food is from the moment they order to the moment it arrives. GPS and order status updates help reduce uncertainty and improve satisfaction.
- GPS Technology: GPS allows accurate location detection, delivery route optimization, and real-time courier tracking. It’s a must-have feature for efficient delivery and driver coordination.
- Push Notifications: These alerts keep users updated on order status, discounts, and promotions. Push notifications also help businesses re-engage users and boost retention.
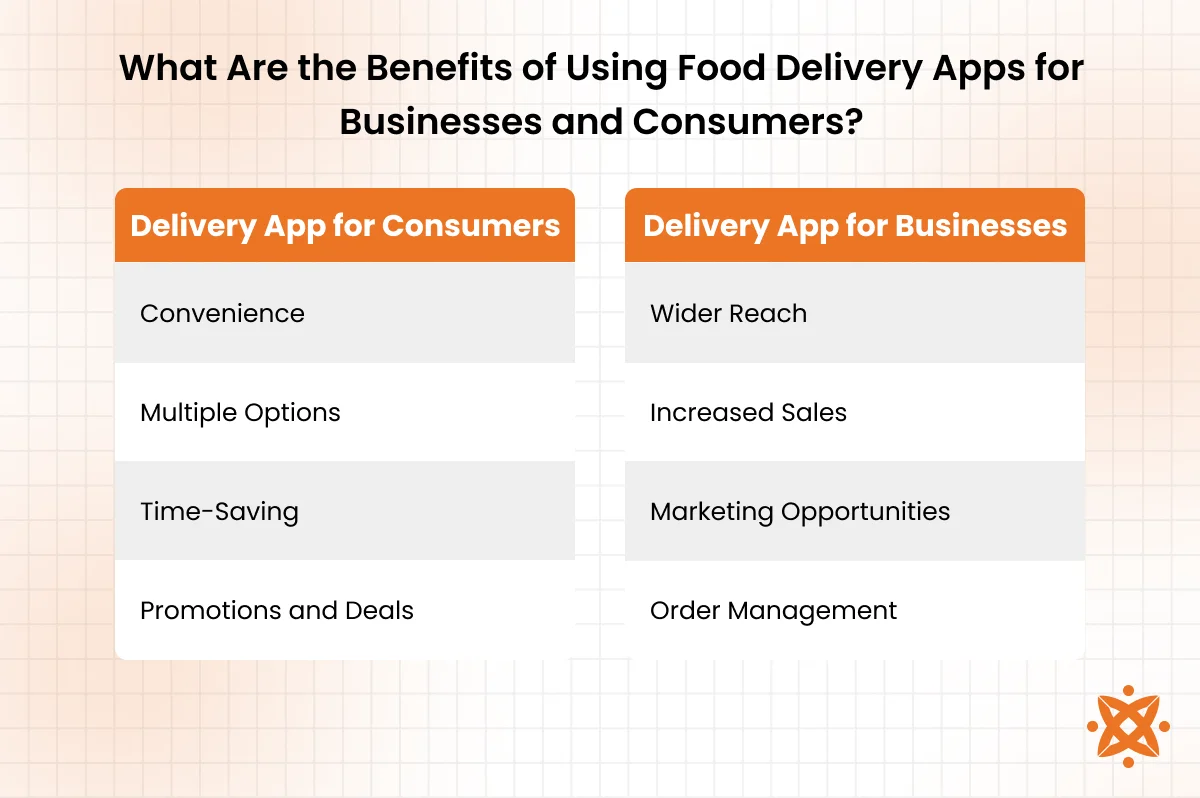
What Are the Benefits of Using Food Delivery Apps for Businesses and Consumers?
The benefits of food delivery apps are convenience, speed, and broader access to meals for users, and increased revenue, visibility, and customer reach for businesses. These apps eliminate the need for physical dining or phone calls, while helping restaurants scale without investing in more physical space.
The following are the benefits of using food delivery apps for businesses and consumers:
Benefits of a Delivery app for consumers include:
- Convenience: You can order food anytime, from anywhere, without leaving your home or calling a restaurant. This is especially helpful during bad weather, busy schedules, or late nights.
- More Options: Food delivery apps give you access to a wide variety of restaurants and cuisines. You’re not limited by distance or neighborhood.
- Time-Saving: Ordering takes just a few taps, and delivery is often quicker than dining out. You can use that saved time for work, rest, or family.
- Promotions and Deals: Many apps offer exclusive discounts, free delivery, or reward points. This helps you save money while enjoying your favorite meals.
Benefits of a delivery app for businesses include:
- Wider Reach: Restaurants can attract customers beyond their immediate location. A food delivery app connects them to people who wouldn’t walk into the restaurant physically.
- Increased Sales: By being available on multiple platforms, businesses can generate more orders without expanding their physical space. More visibility often leads to higher volume.
- Marketing Opportunities: Apps allow restaurants to run promotions, appear in featured listings, or gain reviews. This improves brand awareness and customer loyalty.
- Order Management: Orders come in a structured format, reducing errors from phone calls or in-person rushes. It also helps streamline kitchen workflow and delivery coordination.
How to Design And Develop a Food Delivery App Like Uber Eats and DoorDash?
To design and develop a food delivery app like Uber Eats and DoorDash, you need a solid technology stack, a clean UI/UX design, and a strong focus on cross-platform compatibility for both iOS and Android.
The process involves front-end development for user interfaces, backend development for data handling, API integration for real-time updates, and rigorous testing to ensure smooth functionality and fast performance.
The steps to design and develop a food delivery app like Uber Eats and DoorDash include:
1. Conduct Market Research to Understand the Market Dynamics
Before anything else, you need to understand the competitive landscape. This step involves identifying your target audience, analyzing leading apps like Uber Eats and DoorDash, and studying their features, pain points, and pricing strategies.
Tools like Statista, Google Trends, and App Annie help with market data and user behavior insights. A clear understanding of your market helps you build an app that solves real problems.
2. Define the Essential Features and Functionalities of the App
Once you know the market, the next step is defining what your app will actually do. This includes choosing must-have features like user registration, menu browsing, real-time tracking, and payment integration.
You’ll need to document both customer-facing and admin-side features. Use tools like Miro or Lucidchart for feature mapping and user flows.
3. Design an Intuitive User Interface (UI) and User Experience (UX)
Design is where your idea becomes visible. At this stage, you build clean, intuitive layouts for both mobile and web interfaces using wireframes, mockups, and interactive prototypes. Focus on an easy user journey from search to checkout. Tools like Figma, Adobe XD, and Sketch are commonly used for UI/UX design.
4. Develop the App’s Front-End and Back-End Components
Now it’s time to write the code. For front-end development, you’ll use React Native or Flutter for cross-platform apps, or Swift and Kotlin for native iOS/Android apps. The back-end is where business logic, user data, and APIs live, built using frameworks like Node.js, Django, or Laravel, often hosted on AWS, Firebase, or Heroku. Also, set up RESTful APIs or GraphQL for communication between the front-end and back-end.
5. Test the App Thoroughly to Ensure Quality and Reliability
Testing is non-negotiable. You’ll run unit tests, UI tests, integration tests, and real-device testing to catch bugs, performance lags, and compatibility issues. Use tools like Jest, Selenium, Appium, or Firebase Test Lab to automate and monitor tests. Your goal is to ensure the app works perfectly before launching.
6. Deploy the App to the Market and Monitor Performance
Once testing is complete, you deploy the app to the Apple App Store and Google Play Store. You’ll need to meet their submission guidelines and prepare marketing assets like screenshots, app descriptions, and metadata.
After launch, tools like Google Analytics, Mixpanel, and Crashlytics help you track performance, fix issues, and gather user feedback for updates.
Where Can I Find a Food Delivery App Design Template?
You can find a food delivery app design template at UI8.net, Envato Elements, and Figma Community. These platforms offer ready-to-use UI kits and template packages specifically designed for food delivery apps, complete with screens like onboarding, menu lists, checkout, and order tracking.
For example, on Figma Community, you can search “food delivery UI kit” and find free and premium templates contributed by top designers. On UI8 and Envato, you’ll get fully layered design files with consistent color schemes, icon sets, and typography that save hours of work and help you launch faster with a polished look.
What Tools and Technologies are Used in Food Delivery App Like Uber Eats and DoorDash Development?
The tools and technologies used in food delivery app development, like Uber Eats and DoorDash, include programming languages and frameworks, mapping APIs, payment gateways, cloud platforms, and database solutions. Each component plays a specific role — from building the user interface to securing transactions and managing real-time delivery updates.
The tools and technologies used in food delivery apps like Uber Eats and DoorDash development are explained below:
Programming Languages and Frameworks
The core of any app lies in its codebase. Food delivery apps typically require separate tools for frontend, backend, and mobile development.
Programming languages and frameworks tools include the following:
- Swift: Used for building native iOS apps. It’s fast, safe, and backed by Apple.
- Kotlin: Preferred for Android development. It’s modern, expressive, and interoperable with Java.
- JavaScript: Used for interactive front-end features or with frameworks like Node.js for backend logic.
- Python: A versatile backend language, often paired with Django for rapid development.
Programming framework tools include:
- Node.js: A fast, event-driven backend runtime that handles high traffic.
- Django: A high-level Python framework known for clean architecture and speed.
- Express.js: A minimalist JavaScript framework for building APIs and backend services.
Mapping and Navigation Technologies
Accurate delivery tracking is critical for food apps. These tools power real-time location, routing, and ETA calculations. The tools used for mapping and navigation in food delivery apps include:
- Google Maps API: Offers precise geolocation, mapping, and route planning.
- Mapbox: A customizable map service that supports real-time delivery tracking and driver navigation.
Payment Gateways and Security Tools
Food delivery apps need secure, flexible, and fast payment processing. These tools handle transactions and protect sensitive data.
- Stripe: A developer-friendly payment platform with extensive API support and fast checkout options.
- PayPal: A widely used payment gateway that supports credit cards, debit cards, and wallets.
- Braintree: A PayPal-owned solution offering flexible payment integration and support for global currencies.
- Encryption technologies: Tools like SSL certificates and end-to-end encryption secure user data and transactions.
Backend Infrastructure and Database Solutions
The backend is where all data lives and actions are processed. A strong infrastructure ensures performance, scalability, and data safety. The following are backend infrastructure and database solution tools:
- Cloud platforms: Services like AWS, Google Cloud, or Microsoft Azure provide scalable servers, storage, and monitoring tools.
- Databases: Systems like MongoDB (NoSQL) and PostgreSQL (SQL) handle user data, orders, menus, and delivery history.
What Is The Cost of Developing a Food Delivery App Like Uber Eats and DoorDash?
The average cost of developing a food delivery app like Uber Eats or DoorDash in the U.S. ranges from $10,000 to $500,00 depending on the scope, platform, and required features.
The design and UI/UX phase usually costs between $5,000 and $15,000, covering wireframes, user flows, and visual design for both iOS and Android. Front-end and back-end development take up the bulk of the budget, costing around $20,000 to $100,000, depending on the tech stack, team size, and whether you’re building for a single or cross-platform.
If you want real-time tracking and maps, API integration, and GPS services like Google Maps can add another $5,000 to $10,000 to your budget.
Payment integration and security layers, including tools like Stripe or Braintree, generally range from $3,000 to $8,000. You’ll also need a solid backend infrastructure on cloud platforms like AWS or Google Cloud, which adds setup costs of $5,000 to $15,000, plus monthly server and maintenance fees afterward.
Finally, testing, QA, and deployment costs can fall between $10,000 and $30,000, depending on how thoroughly you test across devices and networks.
These numbers reflect development by U.S.-based agencies or top-tier global teams. Working with offshore developers reduces costs, but impacts speed or quality. The more advanced features you want, such as loyalty systems, machine learning recommendations, or driver performance tracking, the higher the investment.
What Is the Difference Between a Food Delivery App and a Grocery Shopping App?
The difference between a food delivery app and a grocery shopping app is what’s being delivered, how it’s sourced, and the urgency of fulfillment. Food delivery apps like Uber Eats focus on delivering ready-to-eat meals from restaurants, often within 30–60 minutes.
In contrast, grocery shopping apps like Instacart or Amazon Fresh let users order raw food items, household essentials, and pantry goods from supermarkets. These deliveries are scheduled for later in the day or week.
While food apps rely heavily on real-time logistics and hot meal handling, grocery apps focus more on inventory management, substitutions, and larger cart sizes. The user experience also differs: food apps prioritize quick checkout and driver tracking, while grocery apps offer list-building, search by product type, and filters for deals or diet needs.
Each app serves a unique purpose in modern convenience shopping, but the backend systems, delivery models, and customer expectations are quite different.
What Are the Current Market Trends in Food Delivery Apps?
The current market trends in food delivery apps include rapid expansion of ghost kitchens and cloud kitchens, rising use of AI personalization and drone or robot deliveries, and strong growth in the online food delivery market.
Ghost kitchens are delivery-only professional kitchens without storefronts. They are becoming more common, offering efficient, low-overhead ways for businesses to meet demand through food delivery platforms
How Do You Increase User Engagement in a Food Delivery App?
You increase user engagement in a food delivery app by offering personalized experiences, loyalty programs, and push notifications that actually add value. When users get meal suggestions based on their past orders, or timely alerts for limited-time deals, it keeps them coming back without feeling spammed.
Gamified rewards, refer-a-friend bonuses, and easy reorder options also drive repeat use. The key is to keep the user experience smooth and rewarding, from the first tap to the final bite.
How Food Delivery Apps Increase Restaurant Revenue?
Food delivery apps increase restaurant revenue by opening up access to customers far beyond walk-in traffic. Restaurants serve hundreds of additional orders daily without expanding their physical space or hiring extra waitstaff, just by being listed on platforms like Uber Eats or DoorDash.
These apps also help restaurants run promotions, display top-selling items, and collect real-time data on what customers want. With built-in marketing tools, order automation, and loyalty integrations, restaurants improve order volume, reduce overhead, and boost profitability.
What Marketing Strategies are Effective for Promoting Food Delivery Apps?
The most effective marketing strategies for food delivery apps include referral programs, social media campaigns, and in-app promotions. Giving users discounts for referring friends or offering free delivery on the first few orders rapidly expands your user base while encouraging repeat use.
Paid ads on platforms like Instagram, Google, and TikTok also work well, especially when they highlight ease, speed, or savings. Partnering with influencers, showcasing real-time customer reviews, and using geo-targeted ads can boost visibility and downloads in your launch cities.
What Is the Cheapest Food Delivery App In the USA?
The cheapest food delivery app in the USA is DoorDash or Uber Eats, depending on your location, restaurant choice, and whether you use a subscription like DashPass or Uber One. These subscriptions offer $0 delivery fees and discounted service fees for a flat monthly rate, making frequent orders more affordable.
Outside of subscriptions, apps like Grubhub run promo codes and limited-time offers that cut costs. But in general, the total cost depends on the delivery fee, service fee, and restaurant pricing, not just the app itself. Comparing costs per order is the best way to find the cheapest option in your area.
How Do I Choose a Reliable Food Delivery App Development Service?
To choose a reliable food delivery app development service, look for a team with proven experience, a strong portfolio, and clear communication processes. You want developers who understand the food delivery space, offer scalable solutions, and have worked with technologies like real-time tracking, payment integrations, and cross-platform frameworks.
It’s also important to assess their post-launch support, ability to meet deadlines, and transparency on pricing. Reading client reviews, scheduling a discovery call, and asking for a project roadmap before committing helps you avoid costly mistakes. It is important to find a food delivery app development service that aligns with your business goals.
How Do Food Delivery Apps Make Money?
Food delivery apps make money through delivery fees, service charges, restaurant commissions, and subscription plans. Every time a user places an order, the app collects a small cut from the restaurant (usually 15%–30%) and also charges the customer a delivery or service fee.
Many platforms also offer paid premium memberships, like DashPass or Uber One, which provide free delivery in exchange for a monthly fee. Additionally, apps earn from in-app promotions and advertising, where restaurants pay to be featured more prominently on the platform, increasing visibility and sales.
How Is AI Used in Food Delivery Apps?
AI is used in food delivery apps to power personalized recommendations, delivery route optimization, demand forecasting, and customer support automation. When you open the app and see your favorite meals listed at the top, that’s machine learning at work, analyzing your order history and preferences to show what you’re most likely to buy.
On the backend, AI helps reduce delivery time by suggesting the fastest routes using real-time traffic data. It also predicts peak hours and adjusts driver availability or promotional pricing accordingly.
Some apps use AI chatbots for order updates or customer service, making the experience faster and less dependent on human agents.