Android automation testing tools are software frameworks designed to systematically execute test cases on Android applications without manual intervention. These tools are integral in improving testing accuracy and minimizing human error. According to Statista (2025), over 87% of mobile developers integrate automation tools to streamline app testing, citing reduced release cycles and improved user experience.
There are three main types of Android automation testing tools: UI testing tools (e.g., Espresso, UIAutomator), unit testing tools (e.g., JUnit), and end-to-end frameworks (e.g., Appium, Robot Framework). Each type serves a distinct role—from testing individual code components to evaluating the entire app’s user flow.
Dr. James Whittaker, a leading software testing expert and former engineering director at Google, explains: “Automation testing ensures consistency in results, faster feedback loops, and supports continuous integration pipelines—key factors in successful mobile development.”
These tools are measured by their efficiency (test execution speed and reliability), quality (bug detection rate and test coverage), and integration capabilities with CI/CD systems like Jenkins or GitLab. They support parallel testing, test scripting reusability, and cross-device compatibility, making them indispensable for scalable Android development.
What is Android Automation Testing?
Android automation testing is a software testing method that uses automated scripts and frameworks to evaluate the behaviour, functionality, and performance of Android applications.
Developers use automation to replace repetitive manual testing tasks with scripted interactions, ensuring consistent and accurate test results.
In Android automation testing, developers create test cases that simulate real user actions such as tapping buttons, typing text, and navigating screens. These automated interactions validate how the app responds under different scenarios.
The purpose of Android automation testing is to improve accuracy, reduce testing time, and increase test coverage. Manual testing is slow and error-prone. Automated testing runs faster, works across multiple devices, and keeps applications stable after updates. It includes UI testing to verify interface behaviour, functional testing to check component performance, and performance testing to measure responsiveness, stability, and resource usage.
What Are the Benefits of Android Automation Testing?
The benefits of Android automation testing are efficiency, speed, accuracy, scalability, reusability, comprehensive coverage, and support for continuous integration.
- Automation testing improves efficiency by executing test cases faster than manual testing.
- Automation testing increases speed by running tests continuously and providing rapid feedback on code changes.
- Automation testing ensures accuracy by executing predefined scripts without human error.
- Automation testing supports scalability by managing large and complex test suites for apps with extensive functionality.
- Automation testing provides reusability because test scripts can validate multiple app versions and support regression testing.
- Automation testing delivers comprehensive coverage by testing UI, functionality, and compatibility across devices and OS versions.
- Automation testing integrates with CI/CD pipelines, enabling early detection of issues and faster release cycles.
What Are the Top Android App Automation Testing Tools and Frameworks?
Here are some popular Android automation testing tools and frameworks, along with the pros and cons you can consider to choose the most suitable one for your Android project.
Appium
Appium is an open-source automation framework created by Dan Cuellar in 2011, first released as iOSAuto and later extended to Android. It is used for automating native, hybrid, and mobile web applications across Android and iOS. Appium interacts with applications through standard automation APIs that simulate user actions such as taps, text entry, and navigation.
The framework supports multiple programming languages including Java, JavaScript, Python, and Ruby. It enables cross-platform testing and requires a Windows, macOS, or Linux system with Node.js (^14.17.0, ^16.13.0, or ≥18.0) and NPM (≥8). Appium is lightweight in setup and does not need extensive system resources.
The advantages of Appium are support for several languages, compatibility with different app types, and cross-platform use. The limitations are the absence of built-in video recording and the requirement of knowledge in WebDriver and mobile app architecture.
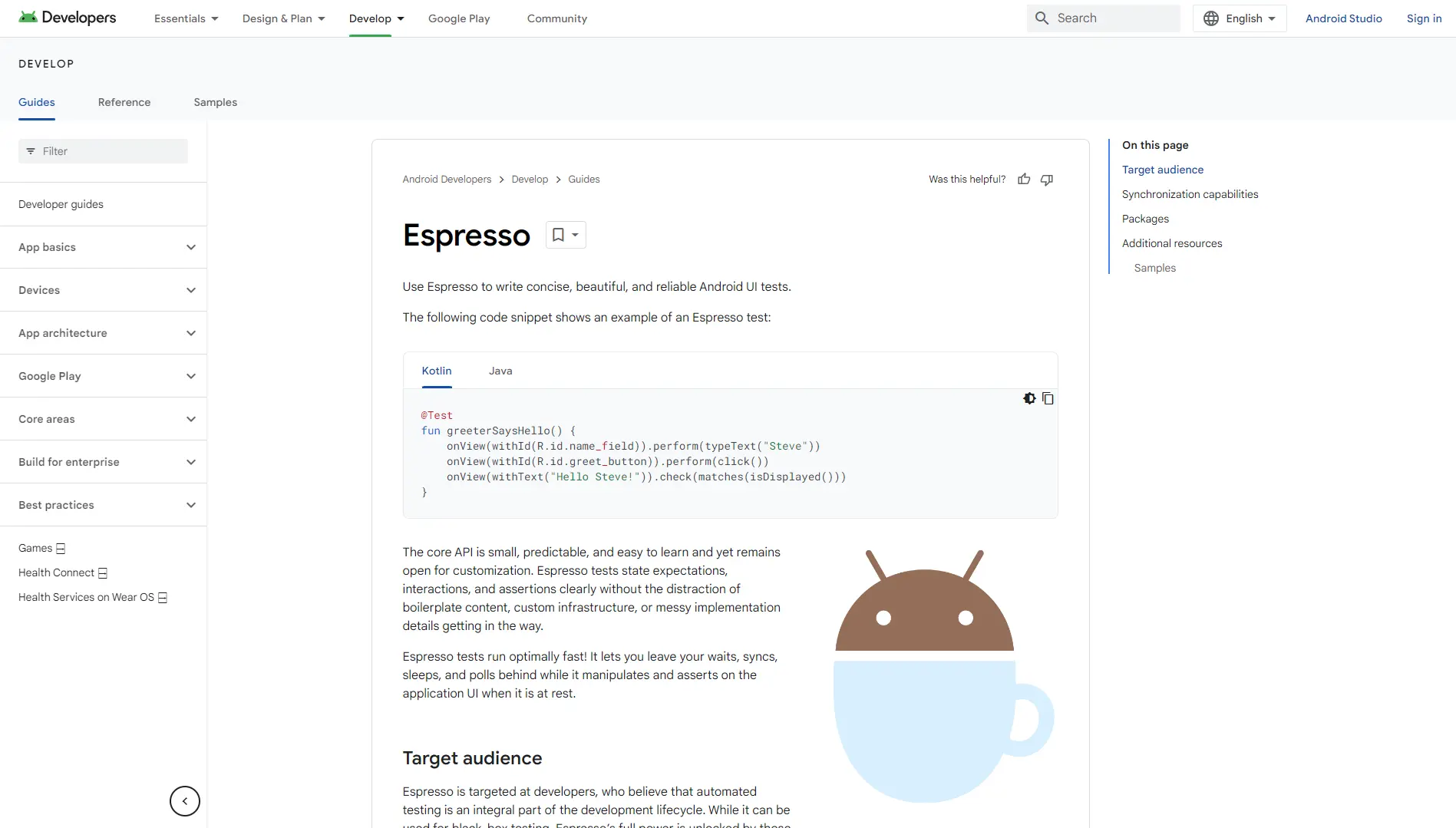
Espresso
Espresso is a testing framework developed by Google for Android UI testing. It provides a fluent API to define and run automated user interaction tests within native Android applications. Espresso integrates with Android Studio and is designed to validate the correctness of UI elements and flows.
Its features include automatic synchronization with the app under test, a predictable and concise API, a set of ViewMatchers and ViewActions for locating and interacting with UI elements, and support for test recording and debugging in Android Studio. The requirements include Android SDK, Android Studio 2.0 or higher, and a device or emulator running Android 4.1 or above.
The advantages of Espresso are reliable synchronization, stable UI testing, and strong integration with Android Studio. The limitations are its restriction to Android-only projects and its focus on UI testing, which excludes other types of testing.
LambdaTest
LambdaTest is a cloud-based testing platform that allows automated and manual testing across operating systems, browsers, and devices. It supports Android automation testing with frameworks such as Selenium, Cypress, TestCafe, Puppeteer, and Playwright.
The platform provides features such as AI-powered test orchestration, access to over 3000 real devices and OS combinations, visual testing to detect UI inconsistencies, and collaboration tools for sharing and reporting results. The requirements include Windows, Linux, or macOS with at least 4 GB RAM and a supported browser version (Chrome ≥60, Edge ≥95, Firefox ≥70, Safari ≥9, Opera ≥60).
The advantages of LambdaTest are scalability, cross-device support, and collaboration functions. The limitation is latency during execution, which can create uncertainty in identifying the source of responsiveness issues.
Robotium
Robotium is an open-source Android automation framework for UI testing. It provides an API that enables developers to create automated tests for Android applications with minimal setup. Robotium supports testing across a wide range of Android devices and OS versions.
The framework supports complex testing scenarios involving multiple apps, integrates with Android Studio and other IDEs, and requires only the Android SDK to run. Test scripts are written in Java, which makes it straightforward for teams already using the language.
The advantages of Robotium are simplicity, multi-app testing support, and broad Android compatibility. The limitations are dependency on Java, narrower documentation resources, and a focus restricted to Android apps.
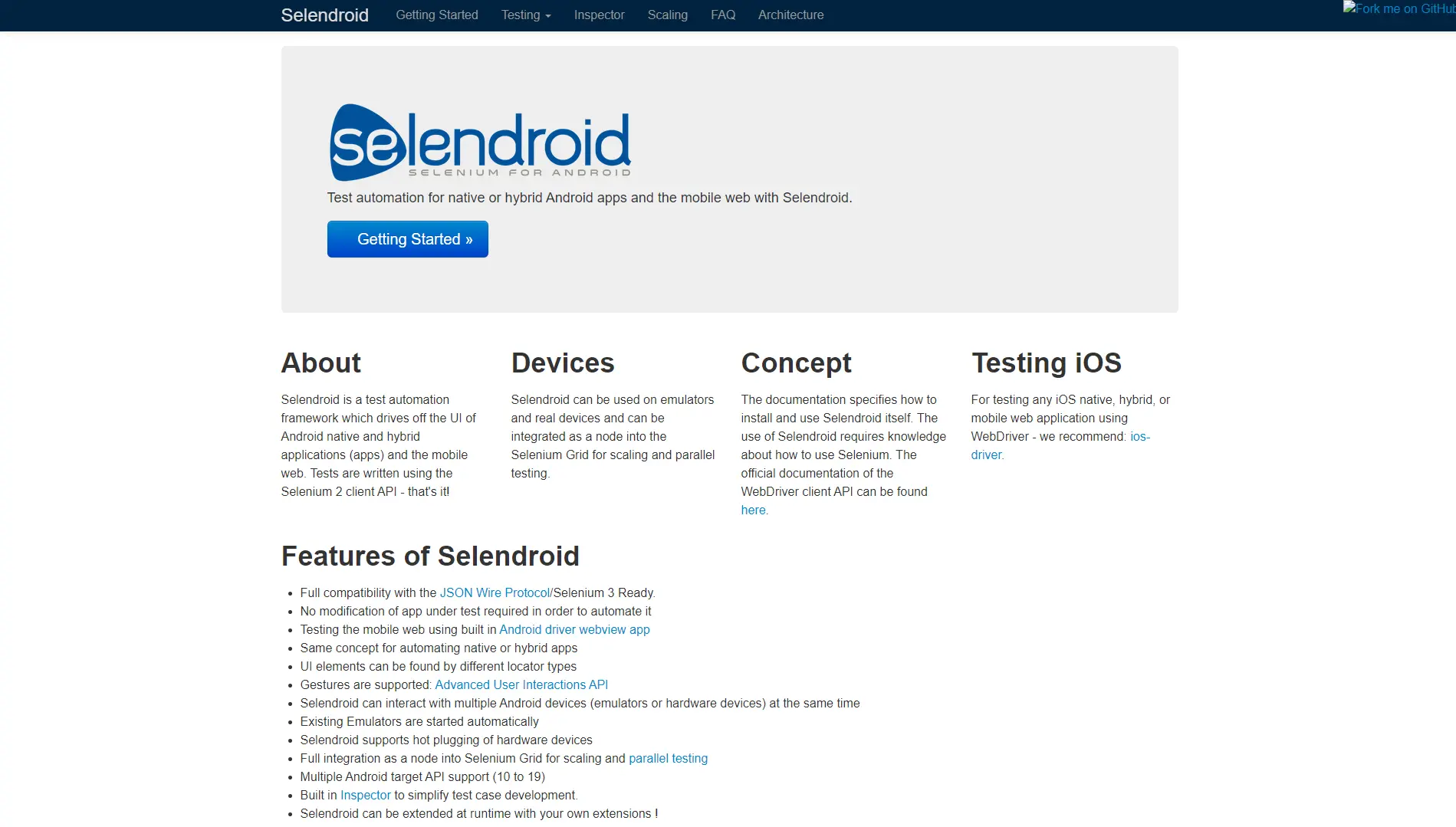
Selendroid
Selendroid is an open-source Android automation framework based on the Selenium WebDriver API. It allows the reuse of existing Selenium test scripts to automate Android applications, covering both native and hybrid apps.
Its features include WebDriver compatibility, support for CI integration with Jenkins, and execution on real devices or emulators. The requirements include Java SDK (≥1.6), Android SDK, configured ANDROID_HOME and JAVA_HOME, and a device or emulator. Selendroid is supported on macOS, Linux, and Windows.
The advantages of Selendroid are compatibility with Selenium, support for native and hybrid Android apps, and integration with CI/CD pipelines. The limitations are a smaller developer community, reliance on Java, and limited support for cross-platform testing.
Which is the best Android automation testing tool for your project?
There is no single best Android automation testing tool. The best tool depends on project requirements, programming language support, cost considerations, and community resources.
Project requirements
Project requirements determine the suitability of a testing tool. The type of application (native, hybrid, or web), the testing objectives (UI, functional, or performance), and compatibility with the development stack define which tool should be used. Espresso supports only native Android applications, so it cannot be applied in cross-platform projects. LambdaTest supports Selenium, so it is suitable for functional and performance testing.
Programming language and integration
Tool selection depends on the programming languages supported by the framework. A team that works with Java, Kotlin, or Python should use a framework that aligns with its coding environment. The tool must also integrate with development infrastructure such as IDEs, version control systems, bug tracking tools, and CI/CD pipelines. Strong integration ensures efficient test creation, execution, and collaboration.
Cost and licensing
Cost affects the adoption of a testing tool. Open-source frameworks provide free access to core features without licensing fees, making them suitable for small teams and budget-limited projects. Commercial or cloud platforms require licensing or subscription costs, but they may include advanced features and support services. Teams must balance cost against functionality.
Community support and documentation
Community size and documentation quality influence the long-term usability of a testing framework. A tool with an active developer community provides troubleshooting resources, shared best practices, and regular updates. Platforms such as GitHub, Stack Overflow, and official documentation serve as indicators of available support. A smaller community limits access to resources and slows problem resolution.
What are the future trends in Android automation testing beyond 2025?
Future trends in Android automation testing include AI-driven autonomous testing, codeless platforms, and cloud-based device grids, which reduce human intervention, accelerate coverage, and address device fragmentation.
Which is better: Appium vs Espresso?
Appium is better for cross-platform and multi-language automation, while Espresso is better for native Android UI testing, which means tool selection depends on project scope and testing objectives.
What is the best tool for UI testing on Android?
Espresso is the best tool for UI testing on Android, which integrates with Android Studio, synchronizes test execution, and provides stable validation of interface elements.
What tools support codeless or low-code mobile testing?
Codeless or low-code mobile testing is supported by tools such as Katalon Studio, TestProject, and LambdaTest, which enable script generation through visual workflows and reduce dependency on advanced coding.
How to integrate automation tests into CI/CD?
Automation tests are integrated into CI/CD pipelines by connecting frameworks like Appium or Espresso with Jenkins, GitHub Actions, or GitLab CI, which trigger execution on each code commit and deliver continuous feedback.
What is the difference between testing on real devices and emulators?
Testing on real devices provides accurate validation of hardware, sensors, and performance, while testing on emulators offers cost efficiency and scalability, which means both methods are complementary depending on project stage.
What is emerging in AI-driven or autonomous testing?
AI-driven or autonomous testing introduces self-healing scripts, defect prediction, and adaptive test case generation, which improve resilience against UI changes and accelerate regression cycles.
How to handle fragmentation of Android devices?
Fragmentation of Android devices is handled through cloud device farms, test orchestration, and compatibility matrices, which ensure coverage across screen sizes, OS versions, and hardware variations.