An Android application is a mobile app designed to run on Android-powered devices, enabling users to perform tasks such as sending messages, streaming videos, or browsing the web.
Android, developed by Google, is a Linux-based operating system that powers over 70% of smartphones worldwide, including devices from manufacturers such as Samsung, Xiaomi, and OnePlus.
According to Business of Apps, the U.S. app market reached a valuation of $44.9 billion in 2023, driven by 12.5 billion downloads and a cumulative usage of 217 billion hours, illustrating the critical demand for optimized Android applications across sectors.
Android application development is the process of building mobile applications for Android-powered devices using programming languages such as Java and Kotlin.
The development process includes planning the project scope, designing the user interface, coding features, testing for bugs, and deploying the app. Each step contributes to ensuring usability and performance.
The cost of developing an Android app varies widely, ranging from $20,000 to $150,000, depending on factors like app complexity, features, and the development team’s location, as studied by Talent.com.
What is an Android Application?
An Android application is software developed to operate on devices running the Android operating system. These applications are created using Android development, primarily in languages like Java and Kotlin, and they run within the Android runtime environment. Android apps cover various functions, such as WhatsApp for communication, Spotify for entertainment, Google Docs for productivity, and PUBG Mobile for gaming.
The history of Android apps began in 2008 when Google launched the first commercial version of the Android operating system with the Android Market (now Google Play Store). Android was initially developed for digital cameras and evolved into a mobile OS after Google acquired Android Inc. in 2005.
The first Android smartphone, the HTC Dream (T-Mobile G1), was released in 2008 and supported third-party applications created with the Android SDK. Over the years, Android has become the world’s most widely used mobile operating system, with popular apps like Instagram, Gmail, and TikTok available for download.
Android was developed by Android Inc., a startup founded by Andy Rubin, Rich Miner, Nick Sears, and Chris White in 2003. However, in 2005, Google acquired the company and continued its development, leading to the first official Android release in 2008. Google has overseen Android’s development, updating it with new features, security improvements, and optimizations to enhance user experience and protect devices.
The executable file of an Android application is called an APK (Android Package) because it bundles the code, resources, and assets needed for installation. The APK file format is used to distribute and install apps on Android devices. An APK file contains all the necessary components of an app, including code, resources, assets, and manifest files. When installed, the Android system processes the APK, ensuring compatibility and security before execution.
According to Global App Testing, the US leads the Android app development market, which was projected to generate $74.83 billion in 2022. The Android app development market globally is expected to generate around $935 billion in revenue in 2025.
What are the Different Types of Android Applications?
The different types of Android applications include Native Android Applications, Hybrid Android Applications, Web-based Android Applications, Game Applications, and E-Commerce Apps.
The different types of Android applications are explained below:
Native Android Applications
Native Android applications are built specifically for the Android operating system using official SDKs and programming languages like Java or Kotlin. They deliver the highest performance, with features such as faster graphics rendering, seamless GPS integration, and access to device hardware like cameras and sensors. According to Android developer reports, over 70% of the top apps on Google Play are built natively for superior speed and functionality. Examples include WhatsApp, Google Maps, and Spotify.
Hybrid Android Applications
Hybrid Android applications combine web technologies such as HTML, CSS, and JavaScript with a native container. Hybrid Android applications allow cross-platform deployment from a single codebase, reducing development time while still giving access to device APIs. Statista’s 2023 survey shows that 46% of mobile developers worldwide prefer cross-platform or hybrid frameworks like React Native and Flutter for faster delivery. Examples include Instagram, Twitter, and Evernote.
Web-based Android Applications
Web-based Android applications run within a mobile browser or lightweight container, often requiring continuous internet connectivity. They are easier to update because changes can be made on the server without requiring app reinstallation, but they offer limited offline functionality. Research by TechTarget highlights that progressive web apps (PWAs) can cut data usage by up to 90% compared to native apps, making them cost-effective for users in emerging markets. Examples include Google Docs, Pinterest Lite, and Flipkart Lite.
Game Applications
Game applications focus on entertainment, ranging from casual 2D games to advanced 3D and AR/VR experiences. They require high-performance graphics, and developers often use frameworks like Unity or Unreal Engine because these game engines optimize rendering and enable complex game mechanics. Newzoo reported that mobile gaming generated $90 billion in revenue in 2023, accounting for 50% of the global gaming market. Examples include PUBG Mobile, Candy Crush Saga, and Clash of Clans.
E-Commerce Apps
E-commerce Android applications enable businesses to sell products or services directly through mobile devices. They integrate features such as product catalogs (Amazon listings), payment gateways (Google Pay, PayPal), and personalized recommendations based on user activity. A BusinessofApps report notes that over 72% of all e-commerce transactions in 2023 were made through mobile apps, driven by Android’s dominant market share. Examples include Amazon Shopping, Flipkart, and eBay.
What are the Features of Android Applications?
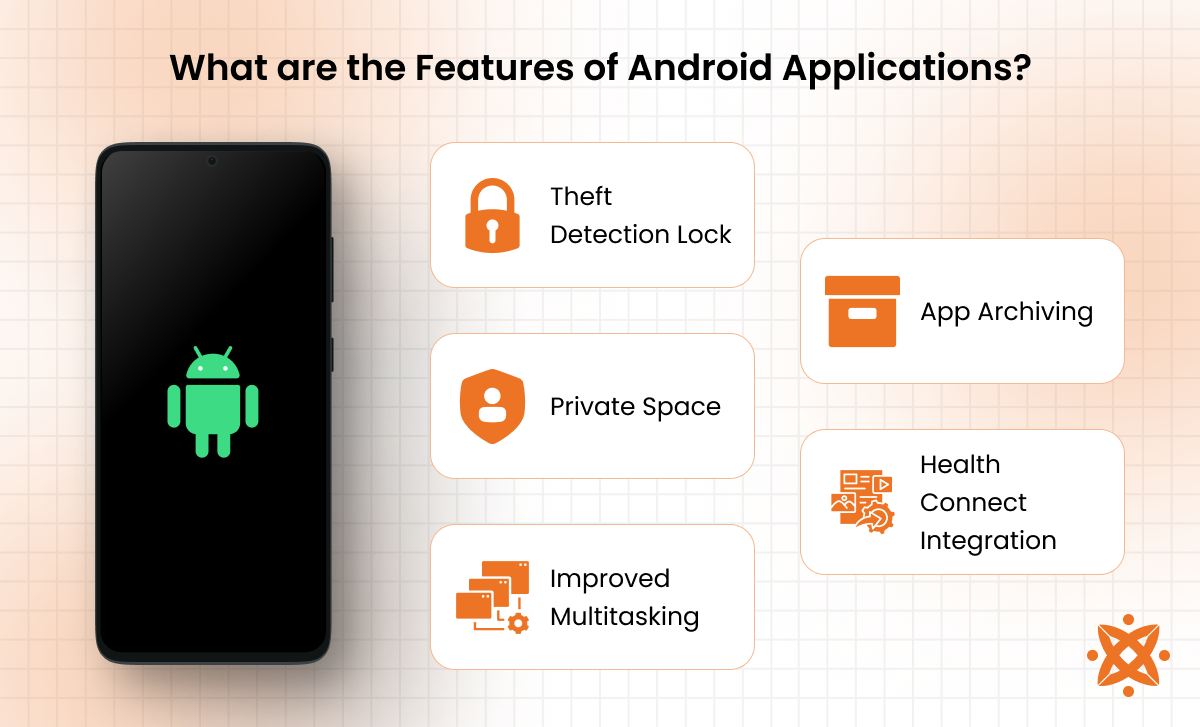
Key features of Android applications include adaptability (apps adjusting to different devices), user-friendly interfaces (such as simple navigation menus), and smooth integration with hardware like GPS and cameras.. These Android app features enable developers to create versatile apps that cater to a wide range of user needs and preferences.
- Theft Detection Lock: This AI-powered feature detects sudden motion or behavior patterns that indicate theft, such as snatching from a user’s hand or rapid movement away from a location. Once triggered, the device automatically locks, preventing unauthorized access to data. This adds an extra layer of protection, reducing the risk of data breaches in case of theft.
- Private Space: Android 15 introduces a Private Space, allowing users to create a hidden, password-protected section within their device. This space stores sensitive applications, such as financial apps, private messaging platforms, or confidential documents. It remains invisible until unlocked, ensuring privacy and security from unauthorized access.
- Improved Multitasking: The update improves multitasking, particularly for foldable devices and tablets. With App Pinning, users keep specific apps in view while switching between multiple tasks. The split-screen and multi-window functionalities have been refined, making it easier to manage multiple apps simultaneously without performance drops.
- App Archiving: Instead of deleting unused apps, users now archive them. This feature helps free up storage space while retaining app data, allowing users to restore archived apps without reinstalling them. This is particularly useful for users who need to manage storage efficiently but don’t want to lose app progress or settings.
- Health Connect Integration: With Android 15, Google has enhanced Health Connect, a unified hub for managing and sharing health and fitness data. This feature allows users to sync health-related data from various fitness apps, smartwatches, and medical devices securely. It also provides better control over data sharing, enabling users to decide which apps access specific health metrics.
- Push Notifications: Push notifications deliver real-time alerts, reminders, and updates directly to a user’s device. They allow Android apps to re-engage users with timely information, such as a banking app sending fraud alerts or a calendar app reminding about meetings. This feature increases retention by keeping users active within the app’s ecosystem.
- Offline Functionality: Offline functionality enables Android apps to store essential data locally so core features work without internet access. Cached content and local storage allow continued use during travel or in low-connectivity areas. This ensures reliability and uninterrupted access.
- Customizable User Interface: Customizable interfaces let users modify layouts, themes, and settings within Android apps. For example, users can switch between dark and light modes or rearrange the home screen layout. This feature enhances usability by aligning the interface with user preferences.
- Integration With Device Hardware: Android apps connect directly with device hardware including GPS, cameras, fingerprint sensors, and accelerometers. This integration supports advanced capabilities such as biometric login, location-based services, and augmented reality. This extends app functionality, enabling experiences such as AR games, health tracking, and secure authentication.
- In-App Payments and Monetization: Android apps integrate with Google Play billing to enable in-app payments, subscriptions, and freemium models. Users make secure transactions without leaving the app environment. This feature provides businesses with reliable monetization options and users with convenient payment methods.
What Are the Pros and Cons of Android Applications?
The main pros and cons of Android applications are listed below:
Pros of Android Applications
- Open-source flexibility: Android’s open-source model allows device manufacturers and developers to modify the system for specific requirements. This flexibility enables innovations such as custom UI layers (e.g., Samsung One UI, Xiaomi MIUI).
- Large market share: With over 70% of the global mobile OS market share in 2024 (StatCounter), Android provides the broadest reach for applications across regions including Asia, Africa, and Latin America.
- Variety of devices: Android applications run on smartphones, tablets, smart TVs, wearables, and IoT devices, ensuring a wide hardware ecosystem.
- Diverse app ecosystem: The Google Play Store hosts 3.5 million apps (Statista, 2024), covering categories from social networking and e-commerce to finance and healthcare. This diversity enhances accessibility for users and monetization opportunities for businesses.
Cons of Android Applications
- Fragmentation: The wide range of device types and OS versions complicates testing and updates. Developers often need to support older versions still active in markets, increasing development costs.
- Security risks: Android’s open ecosystem exposes it to higher risks of malware and unauthorized app distribution. A Kaspersky report found that Android accounted for 86% of mobile malware infections in 2023.
- Revenue gap: Despite its large user base, Android apps generate lower average revenue per user compared to iOS. Data.ai reports that iOS users spent nearly twice as much as Android users on apps in 2023.
- Performance variation: Device quality varies widely across manufacturers, leading to inconsistent app performance. High-end devices deliver smooth experiences, while low-end models may face lag and crashes.
What is Android Application Development?
Android application development is the process of creating applications that run on devices powered by the Android operating system.This involves designing, coding, testing, and deploying applications distributed through the Google Play Store or other platforms. Developers use Android development techniques to build feature-rich, efficient, and scalable applications for use cases such as business tools (Slack), entertainment (Spotify), and productivity apps (Google Drive).
Who is an Android Developer?
An Android developer is a software professional who specializes in designing, building, and maintaining applications for devices running the Android operating system. These developers use Android software development techniques to create apps for various purposes, from social networking and gaming to business and healthcare solutions.
Android app developers are responsible for writing efficient code, debugging applications, optimizing performance, and ensuring compatibility across different Android devices. They integrate features like authentication, databases, push notifications, and real-time updates with APIs, third-party libraries, and backend services. Android developers follow UI/UX guidelines to create user-friendly interfaces that improve accessibility and user satisfaction.
An Android developer must have expertise in Kotlin and Java, the primary programming languages for Android apps. Knowledge of C++ is beneficial for performance-intensive applications. They must also be proficient in Android Studio, the official IDE, and frameworks such as Jetpack, Compose, and Retrofit for UI development and networking. Familiarity with Firebase, RESTful APIs, and SQL/NoSQL databases is necessary. Other valuable skills include using version control systems (Git), writing unit and UI tests, and understanding Android security best practices.
An expert Android developer builds various types of applications, including e-commerce apps, social media platforms, gaming applications, fintech solutions, healthcare apps, educational tools, and enterprise applications. Depending on their expertise, they develop cross-platform apps using frameworks like Flutter or React Native to extend their reach beyond Android devices.
How To Develop an Android Application?
To develop an Android app, a developer follows a process of designing, coding, testing, and deploying the application using Android development techniques. Android application development ensures the app is functional, user-friendly, and optimized for different devices.
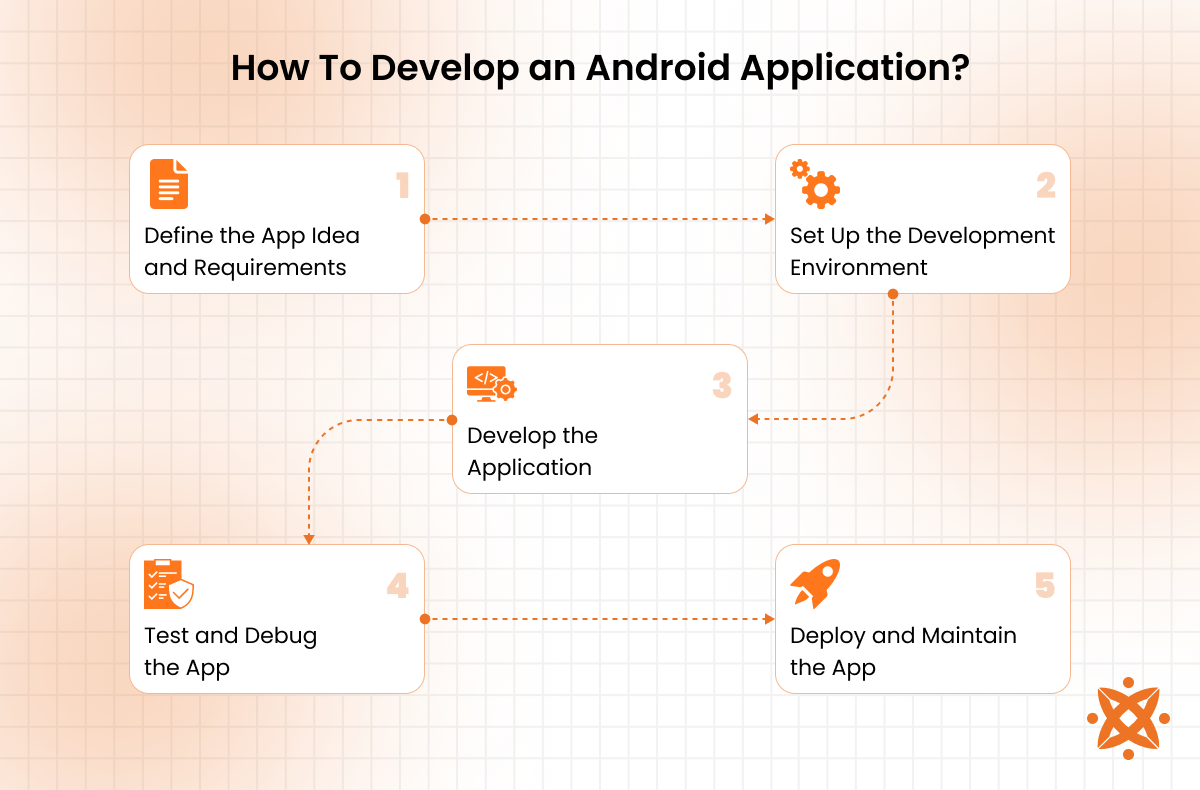
To develop an Android app, the following steps are implemented:
1. Define the App Idea and Requirements
The first step is identifying the app’s purpose, target audience, and core features. Developers conduct market research to analyze competitors and user needs. Creating wireframes and mockups helps visualize the app’s layout and functionality before development begins. Tools like Figma or Adobe XD are used for UI/UX design.
2. Set Up the Development Environment
Developers install Android Studio, the official IDE for Android development, and configure the Android SDK. They select a programming language, Kotlin or Java, to write the app’s code. Version control systems like Git (via GitHub or GitLab) are set up to manage code efficiently at this stage.
3. Develop the Application
The development phase involves coding the app’s frontend (UI) and backend (logic and database). Before coding begins, the database schema and backend architecture should be finalized to ensure scalability. Developers use Jetpack Compose or XML for UI design, Retrofit for API integration, and Room Database or Firebase for data storage. Example: A food delivery app requires user authentication, real-time tracking, and a payment gateway.
4. Test and Debug the App
Testing ensures the app functions as expected across different devices and Android versions. Developers use JUnit for unit testing, Espresso for UI testing, and Android Emulator or real devices for performance testing. Debugging tools in Android Studio help identify and fix errors. Example: Testing a social media app for image uploads and notifications.
5. Deploy and Maintain the App
Once testing is complete, the app is packaged into an APK or AAB file and submitted to the Google Play Store. Developers follow Play Store guidelines, apply App Store Optimization (ASO) techniques such as keyword-rich titles, descriptions, and visuals to improve discoverability, and monitor analytics for user feedback. Continuous updates and security patches ensure the app remains secure, stable, and aligned with user expectations. Example: An e-commerce app adding new payment methods after launch.
What is the Android Operating System?
The Android operating system is a Linux-based platform developed by Google for smartphones, tablets, and smart devices. It combines open-source components with proprietary services such as the Google Play Store. Core parts of Android are written in Java, C++, and C, while Kotlin is the primary language for app development. As of 2025, the latest version is Android 14, which introduces predictive back gestures, stronger app permission controls for privacy, and improved multitasking support for foldable devices.
Which Frameworks Support Android Applications?
Frameworks that support Android applications include Android Jetpack, Flutter, React Native, Xamarin, Ionic, Apache Cordova, and Unity. These Android application development frameworks provide necessary tools, libraries, and pre-built components that simplify the development process, enhance performance, and support cross-platform compatibility where needed.
Frameworks that support Android applications are as follows:
- Android Jetpack
- Flutter
- React Native
- Xamarin
- Ionic
- Apache Cordova
- Unity
What Are the Latest Trends in Android Development?
The latest trends in Android development include AI and ML integration, adoption of 5G technology, cross-platform frameworks such as Flutter and React Native, stronger security enhancements, and the use of AR and VR. These trends are shaping the future of mobile applications by improving personalization, enabling faster data transfer, and supporting immersive features like AR gaming.
Integrating AI and ML into Android apps allows for more personalized and intuitive user experiences. Developers use these technologies to create smarter applications, such as shopping apps that recommend products based on browsing history or fitness apps that adjust routines dynamically.
The widespread adoption of 5G technology revolutionizes Android app development by providing faster data transfer rates and lower latency. The adoption of 5G enables developers to build responsive, data-intensive apps such as high-quality streaming platforms, cloud gaming, and real-time analytics tools.
Cross-platform development frameworks, such as Flutter and React Native, are gaining popularity among developers. These frameworks allow developers to build applications that run on multiple platforms, reducing development time and costs while maintaining native-like performance and user experience.
Security remains a top priority in Android development. Developers are implementing advanced security measures, including biometric authentication and blockchain technology, to protect user data and ensure privacy. This focus on security is important as cyber threats such as phishing attacks, ransomware, and unauthorized app distribution continue to grow.
AR and VR technologies in Android applications are expanding, offering immersive experiences in gaming, education, and retail. These technologies provide users with environments such as AR-powered retail try-ons, VR classrooms, and immersive 3D games, enhancing the overall user experience.
What is the Difference Between Android App Development and iOS App Development?
The main difference between Android app development and iOS app development is the operating system they are built for. Android apps run on Google’s Android OS, while iOS apps run on Apple’s iOS. This distinction affects various aspects of development, including programming languages, development tools, design guidelines, and app distribution.
Android apps are primarily developed using Kotlin or Java, while iOS apps are built with Swift or Objective-C. Android development relies on Android Studio, whereas iOS development uses Xcode. Another key difference lies in the app store policies. Android apps are published on the Google Play Store, which has a relatively lenient review process, while iOS apps go through a stricter approval process on the Apple App Store.
From a design perspective, Android follows Material Design, allowing customization across different manufacturers, while iOS follows Human Interface Guidelines for consistent design across Apple devices.
Android and iOS app development also differ in market reach. Android has a larger global user base, especially in developing regions, while iOS dominates in markets like the US and Europe with higher revenue potential. These differences impact how developers approach building, optimizing, and monetizing applications for each platform.
What Is the Architecture of an Android App?
The architecture of an Android app defines how different components interact to ensure scalability, maintainability, and efficiency. Android applications follow a multi-layered architecture with components for UI (Activities), data handling (Content Providers), and system interactions (Services, Broadcast Receivers).
At its core, Android architecture is based on four main components: Activities, Services, Broadcast Receivers, and Content Providers. Activities manage the user interface and interactions, ensuring smooth navigation between different screens. Services handle background processes, such as music playback or notifications, running independently of the UI.
Broadcast Receivers enable the app to respond to system-wide broadcast events, like battery status or network changes. Content Providers manage data sharing between apps, allowing access to stored content such as contacts, files, or databases.
Modern Android development follows recommended architecture patterns such as MVVM (Model-View-ViewModel) and MVP (Model-View-Presenter) to separate concerns and improve code organization. These principles ensure that Android apps are modular (features built independently), responsive (smooth UI interactions), and adaptable to screen sizes on devices such as phones, tablets, and foldables.
What is the Average Salary of an Android Application Developer?
The average salary of an Android application developer in the United States is approximately $126,357 per year, or $60.75 per hour, according to Talent.com. Entry-level positions start at around $104,984 annually, while experienced developers earn up to $159,984 per year. Globally, salaries vary based on factors such as location (e.g., US vs. India), years of experience, and demand in regional markets. In the U.S., the higher cost of living and strong demand for tech talent contribute to these elevated salary figures.
Can I Create an Android App without Coding?
Yes, it is possible to create an Android app without coding. No-code platforms like Adalo and Thunkable allow users to design and develop apps using visual interfaces and pre-built components, eliminating the need for traditional programming knowledge. These tools are useful for individuals or businesses that want to quickly prototype or deploy applications without investing in extensive development resources.
Is it Possible to Develop Android Apps with Python?
Yes, it is possible to develop Android apps using Python. Frameworks like Kivy and BeeWare enable developers to write Android applications in Python, offering an alternative to Java or Kotlin. These frameworks have lower performance and limited access to native features compared to traditional Android tools, and their communities and support resources are smaller.
Can I Build Android Apps Using React Native?
Yes, you can build Android apps using React Native. Developed by Facebook, React Native is a popular framework that allows developers to create cross-platform applications for both Android and iOS using JavaScript and React. It provides near-native performance and a rich set of pre-built components, making it a preferred choice for companies like Facebook and Shopify that maintain a single codebase across Android and iOS.
Can I Build Android Apps Using Flutter?
Yes, you can build Android apps using Flutter. Flutter is an open-source UI toolkit developed by Google that enables developers to create natively compiled mobile, web, and desktop applications from a single codebase. It uses the Dart programming language and offers customizable widgets, enabling fast development and flexible UI design.
Can I Build Android Apps Using Xamarin?
Yes, you can build Android apps using Xamarin. Owned by Microsoft, Xamarin is a cross-platform development framework that allows developers to create Android and iOS applications using C#. It provides access to native APIs and tools, enabling the creation of high-performance applications with a native look and feel. Xamarin.Forms enables a single UI to be shared across platforms, simplifying development.
How to Choose an Android App Development Company?
Choosing the right Android app development company depends on factors such as expertise in frameworks like Flutter and React Native, a proven portfolio with successful apps, positive client reviews, and knowledge of tools like Android Studio.